Question
Question: What are Claisen Schmidt's condensation and Kolbe's Reaction? Give one example of each....
What are Claisen Schmidt's condensation and Kolbe's Reaction? Give one example of each.
Solution
Claisen Schmidt condensation is the chemical property of aldehyde and ketone. It is based on a cross aldol condensation reaction. Kolbe's reaction is based on the chemical property of phenol. Salicylic acid is the major product of Kolbe's reaction.
Complete answer:
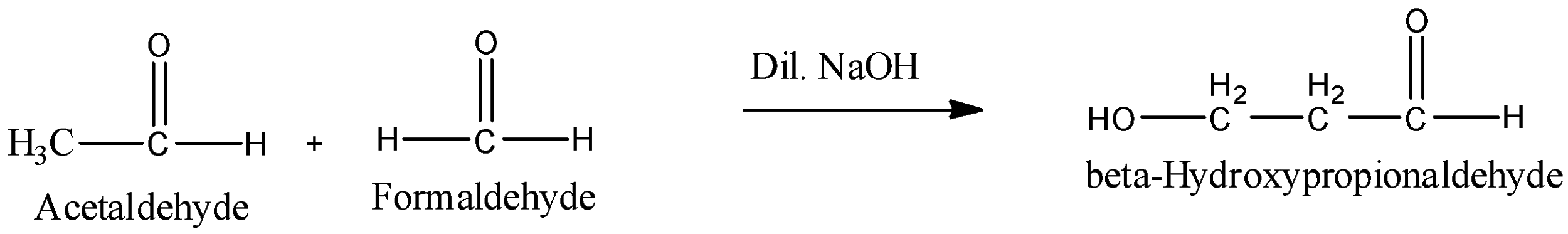
Aldol condensation is not confined to the condensation of two molecules of the same aldehyde or ketone (self-condensation). It can also take place between two different aldehydes or ketones or between one aldehyde and one ketone. Such an aldol condensation between two different aldehydes or two ketones or between one aldehyde and one ketone is called the cross aldol condensation. For example Reaction between Acetaldehyde and Formaldehyde forms beta- hydroxypropionaldehyde.
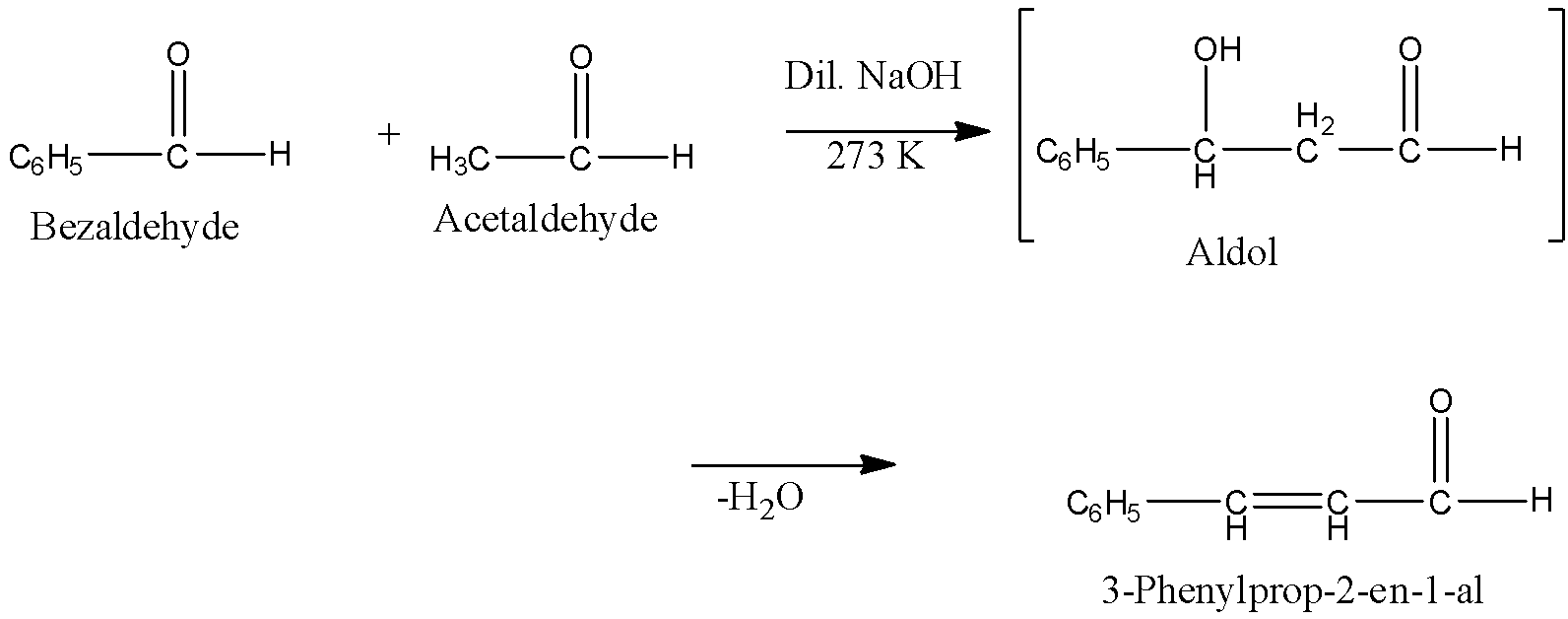
Claisen Schmidt condensation: When a base-catalyzed cross aldol condensation between an aromatic aldehyde and an aliphatic aldehyde or a ketone is called Claisen Schmidt condensation or simply Claisen reaction. For example, Benzaldehyde reacts with Acetaldehyde to form 3-Phenylprop-2-en-1-al.
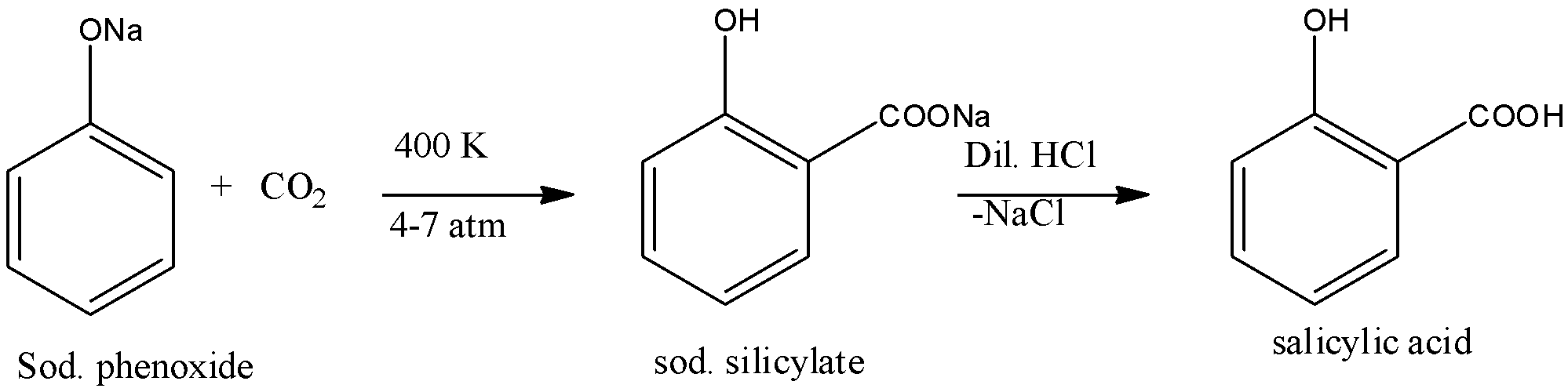
Kolbe’s Reaction: Sodium phenoxide when heated with carbon dioxide at 400 K under a pressure of 4-7 atmospheres followed by acidification gives 2-hydroxybenzoic acid ( salicylic acid) as the main product with a small amount of 4-hydroxybenzoic acid. This reaction is called Kolbe’s reaction. The reaction is given below:
Note: The salicylic acid which is prepared from Kolbe's reaction is used for the preparation of aspirin, which is widely used for relieving pain and to bring down the body temperature. Even aliphatic esters containing alpha-hydrogen atoms can undergo Claisen Schmidt Condensation on treatment with an aromatic aldehyde in the presence of a base.
