Question
Question: What are cis and trans isomers?...
What are cis and trans isomers?
Solution
In terms of stereochemistry, we can define stereoisomerism as kind of isomerism where molecules contain same molecular formula and sequence of atoms which are bonded whereas in the three dimensional space, the way in which the atoms are arranged would be different. We should know that the two kinds of stereoisomers are geometric isomers and optical isomers.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us first see what is a geometrical isomer?
We have to know that the two carbon atoms are combined by means of double bond, the opportunity of rotation stops to exist. As such the two carbon atoms are fixed concerning one another and rotation must be achieved by turning the molecule all in all. This is known as the idea of confined rotation around the carbon double bonds. Because of this limited rotation two distinct arrangements of the substituted groups appended to these two carbon atoms, become conceivable. Such isomers which force a similar structural formula yet contrast in arrangement in space around the double bond or some other comparable element are known as geometrical isomers.
We have to know that there are two kinds of geometrical isomers namely cis isomer and trans isomer.
- Cis-isomer is the isomer in which same groups are found on same side of the double bond.
- Trans isomer is the isomer in which the same groups are found on the opposite side of the double bond.
For example, let us take the molecule 1,2−dichloroethene. This molecule has two stereoisomer namely cis−1,2−dichloroethene and trans−1,2−dichloroethene .
We can draw the structure of the stereoisomer of 1,2−dichloroethene as,
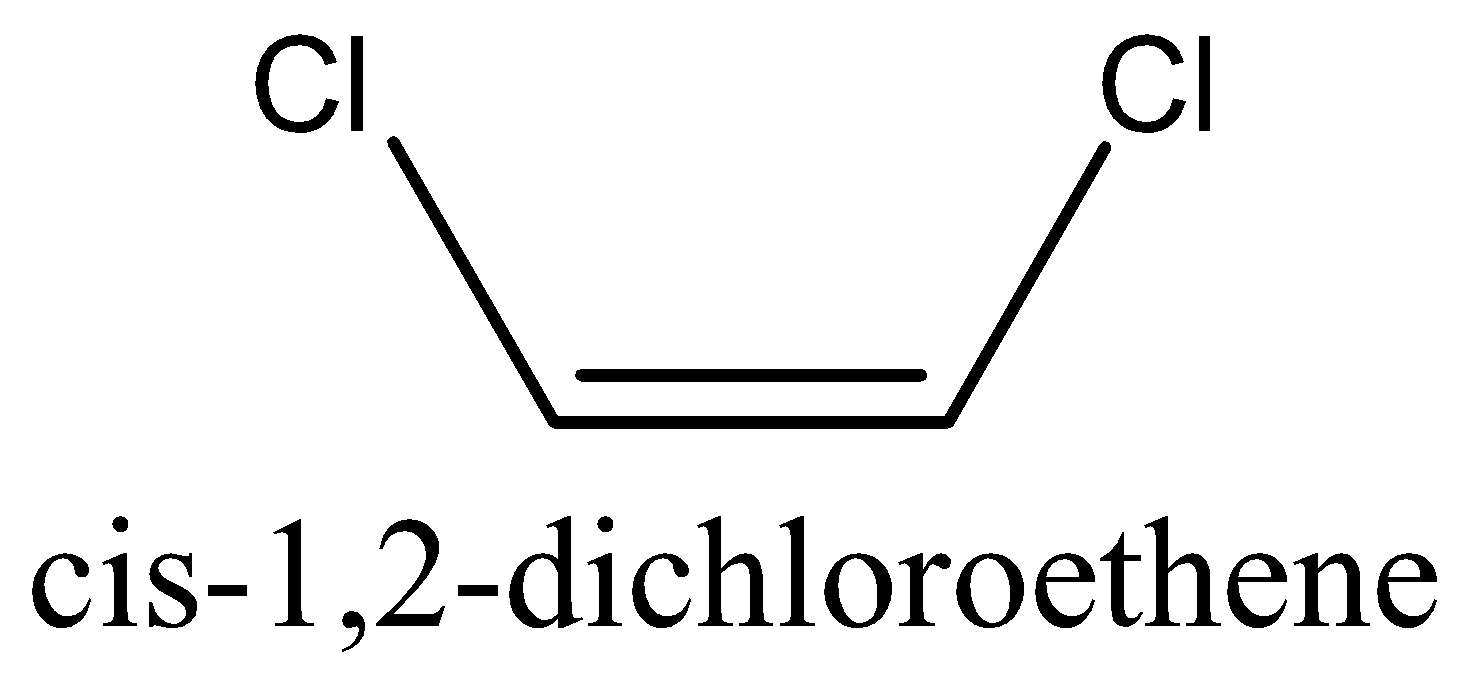
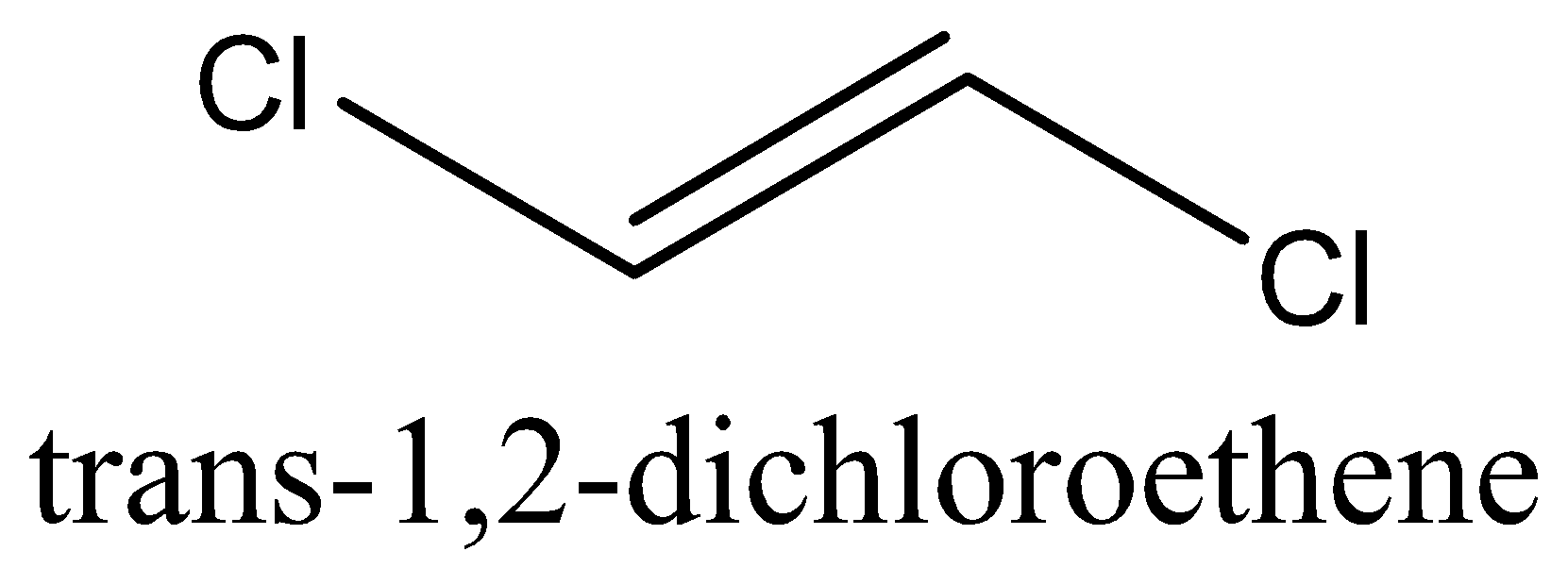
Note: In several cases, the cis-trans isomers of a compound have distinctive physical properties. These distinctions can emerge because of the distinction in the dipole moment of the particle or because of the distinction in the spatial orientation of molecules (or) atoms. Generally, the boiling points of cis isomers would be less than trans isomers.
