Question
Question: What are chelates? Give one example and write the importance of chelate?...
What are chelates? Give one example and write the importance of chelate?
Solution
A ligand is a molecule or an ion that is attached to the metal atom by a coordinate bonding. It donates its electron pair to form a complex. Ligands can be anionic, cationic, or neutral. Ligand acts as a Lewis base and the central metal atom acts as Lewis acid. The examples of ligands are NO + , F - , NH3, etc, There are different types of ligands called as monodentate, bidentate, polydentate depending on the binding sites. If the ligand is bonded to the metal through one atom, it is called a monodentate ligand. Bidentate ligands have 2 atoms that can bind to the central atom at 2 points. This means that it can donate 2 pairs of electrons.
Complete step by step answer:
Now, we know what a bidentate ligand is. Here, the Ligand has 2 donor sites.
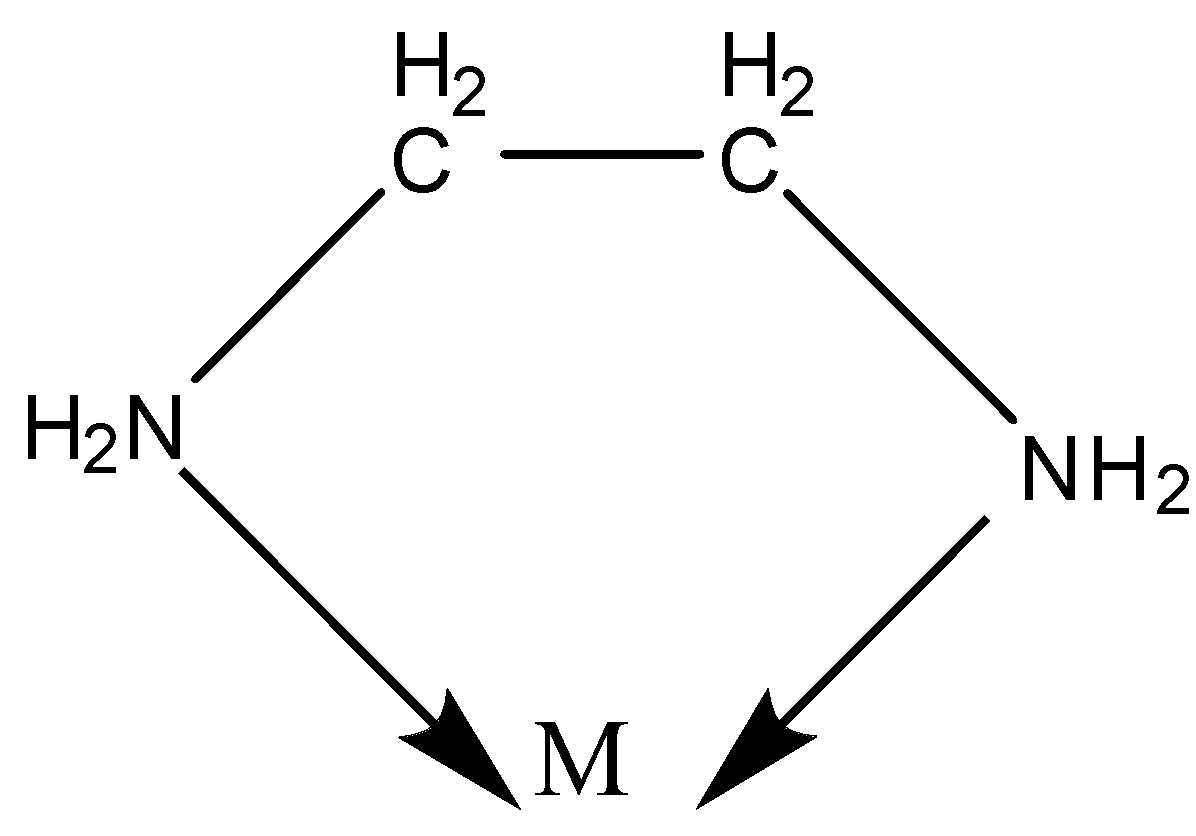
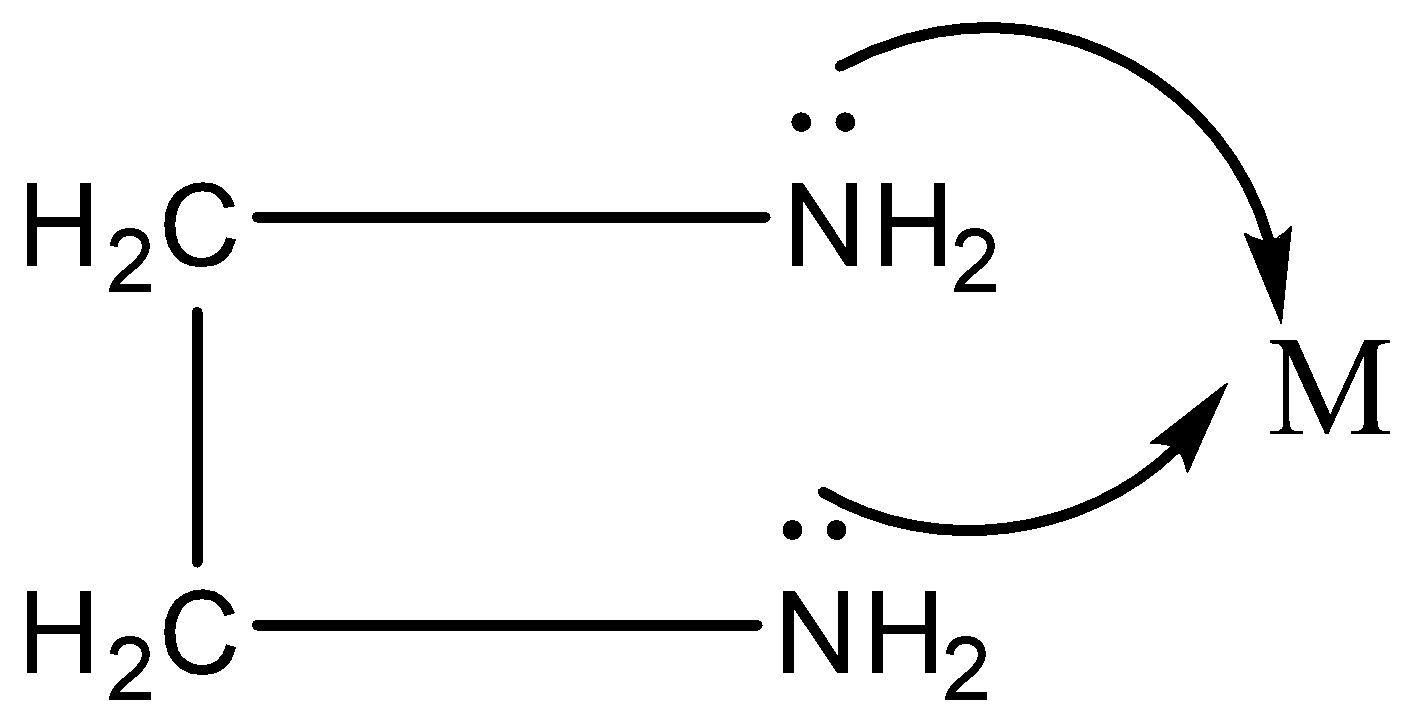
Example:- en- ethylenediamine.
NH2–CH2–CH2–NH2
We know there is one lone pair of electrons on both the N atoms.
Thus, both the N can be coordinated to the central metal atom.
Another example of the polydentate ligand is ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) which is a hexadentate ligand. It leads to the formation of the ring.
Chelation is a process in which a bidentate or a polydentate ligand binds to the metal atom to form a ring.
The complex formed by this process is called a chelate.
The polydentate ligand which leads to chelation is called a chelating agent.
The importance of chelate is:-
It is used in chelation therapy to remove toxic substances from the body (in lead poisoning)
It is used as a contrast agent in MRI scanning.
It is used in chemical water treatments to remove metals.
They can also be used to separate lanthanides and actinides.
Note: As we discussed monodentate ligand donates a lone pair of electrons and bind to the central atom at one point. [Cu(NH3)6]2 + . Here each NH3 group is linked to the metal by only one atom. In the above complexes, ” → ” shows the coordinate bond. A complex [CaNa2EDTA] is given to a person who has consumed lead. The lead present in the bloodstream forms a complex [PbNa2EDTA] and Ca is left behind. [PbNa2EDTA] is more stable and complex and excreted. The chelating complex also has an application in agriculture.
