Question
Question: What are antibodies? Describe the product of methodology (manufacture) of antibodies from microbes....
What are antibodies? Describe the product of methodology (manufacture) of antibodies from microbes.
Solution
Antibodies are proteins that develop in the body in response to various types of infections. Antibodies are specific for different infections - as part of the immune response, the antibody attaches to specific parts of the pathogen so as to destroy it. There are a number of microbes that are used to produce these antibodies.
Complete answer:
Antibodies produced by microbes are regarded as one of the most significant discoveries of the twentieth century and have greatly contributed to the welfare of human society. Anti is a greek word that means "against" and bio means "life", together means "against life"; whereas with reference to human beings, they are "pro-life" and not against. Antibodies are chemical substances, which are produced by some microbes and can kill or retain the growth of other microbes.
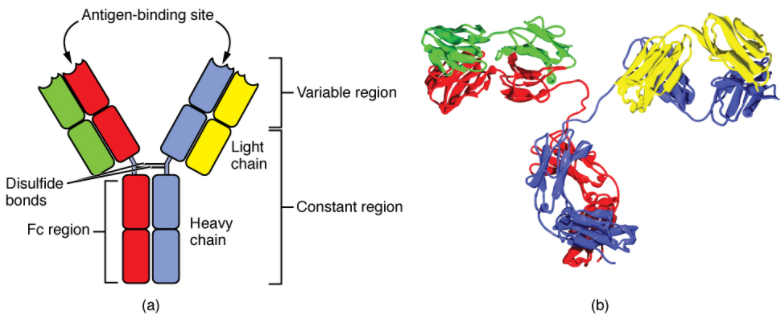
They are also known as "immunoglobulin" which is a large, Y-shaped protein that is used by the immune system so as to neutralize foreign objects such as bacteria, viruses and fungus. They recognise the unique molecule of the pathogen that is called the antigen. They are heavy proteins of about 10 nm in size that are arranged in three globular regions that roughly are Y shaped.
Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) and antibody fragments represent the most important biopharmaceutical products today that are produced from microbes. As the full length antibodies are glycosylated, mammalian cells that allow human-like N-glycosylation are nowadays used for their production.
However, mammalian cells have several drawbacks when it comes to bioprocessing and scale-up, resulting in long processing times and elevated costs. But when we talk about the antibody fragments that are not glycosylated can still exhibit antigen-binding properties and they can be produced in microbial organisms as they are easy to manipulate and cultivate.
The three main microbes used in antibody and antibody fragment production are namely Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Pichia pastoris, and Escherichia coli.
Note: Penicillin was the first antibiotic to be discovered. Alexander Fleming while working on Staphylococci bacteria observed a mould growing in unwashed culture plates around this bacteria. He found out that it was due to a chemical produced by the mould and he named it Penicillin after the mould Penicillium notatum.
