Question
Question: What are 3 sorts of endocytosis?...
What are 3 sorts of endocytosis?
Solution
Endocytosis is a cellular process that involves bringing substances into the cell. An area of the cell membrane surrounds the material to be internalized, which then buds off inside the cell to form a vesicle containing the ingested material. It is an active mode of transportation.
Complete answer:
Endocytosis is the system of internalization of medication inside the cell.
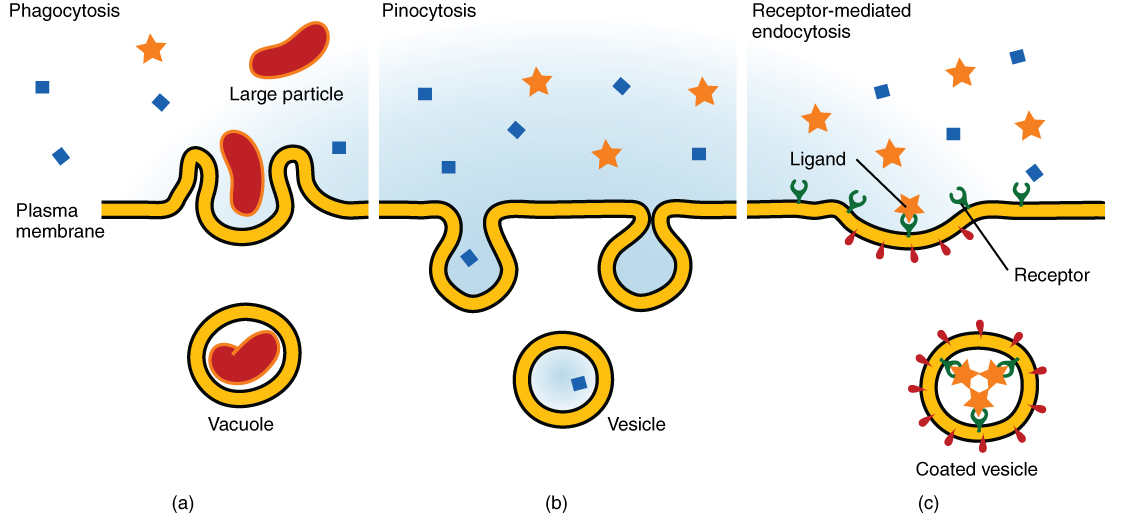
The 3 forms of endocytosis are:
1. Pinocytosis: the ingestion of liquid into a cell by the budding of small vesicles from the cell membrane (0.5–5 m in diameter) filled with a large volume of extracellular fluid and molecules within it (equivalent to 100 CCVs). It usually occurs from highly ruffled regions of the plasma membrane. The pocket filling takes place in an ad hoc manner. The vesicle then enters the cytosol and joins up with other vesicles like endosomes and lysosomes.
2. Phagocytosis: Phagocytosis is the process by which cells bind and internalize particulate matter with a diameter greater than 0.75 m, such as dust particles, cell debris, microorganisms, and apoptotic cells. Unlike clathrin-mediated endocytosis and the caveolae pathway, these processes involve the uptake of larger membrane areas.
3. Receptor-mediated endocytosis: Clathrin-mediated endocytosis is characterized by the formation of small (100 nm in diameter) vesicles with a morphologically distinctive coat of the cytosolic protein clathrin. Clathrin-coated vesicles (CCVs) are found in almost all cells and form clathrin-coated pits, which are plasma membrane domains.
Mammalian cells' endocytic pathway is divided into membrane compartments that internalize molecules from the plasma membrane and either recycle them back to the surface (as in early endosomes and recycling endosomes) or sort them for degradation (as in late endosomes and lysosomes).
Note:
The primary goal of exocytosis is to expel material from the cell into the extracellular fluid, which is the polar opposite of endocytosis. Waste material is encased in a membrane and fuses with the interior of the plasma membrane during exocytosis.
