Question
Question: Virion is - (a)Virus in the stage of multiplication (b)Virus attached to the host cell nucleus ...
Virion is -
(a)Virus in the stage of multiplication
(b)Virus attached to the host cell nucleus
(c)Virus inside the cytoplasm of the host cell
(d)Virus in a cell-free environment
Solution
The virion is a version of a virus that is present in a particular medium. There is a marked difference between virion and viruses depending on their location and their stage of infection.
Complete answer:
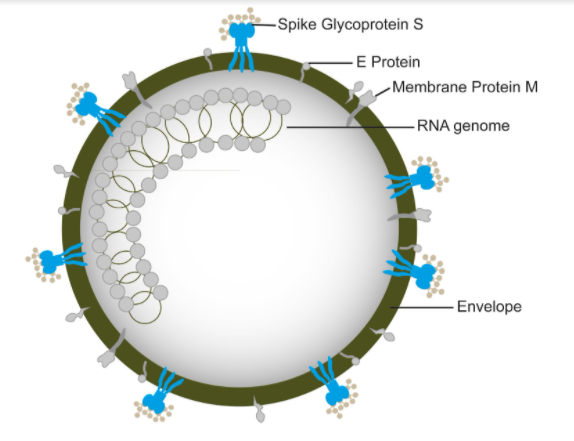
- The virion is the entire virus particle that consists of an outer protein shell known as capsid and an inner core of nucleic acid which is either DNA or RNA.
- The virion capsid protects the genetic material and other proteins. It also confers specificity to the virus. The genetic material and proteins form the core which confers infectivity.
- Virions are formed in the virus production factories or the cytoplasm of the host cells.
Additional Information: - A virus requires a living host cell to multiply.
- They follow two types of the life cycle - the lytic cycle or the lysogenic cycle.
- The viral structure may also contain a coat or envelope made of proteins or enzymes.
- Many of them are icosahedral in shape with regularly arranged units called capsomeres. Virions of plants are rod-shaped and the capsid is naked and cylindrical.
- Since viruses are extremely submicroscopic in size, they can be physically probed by an Atomic Force Microscope (AFM).
So, the correct answer is ‘Virus in a cell-free environment’.
Note: - Sometimes, the structure of the virion may include glycoprotein spicules.
- Virions are different from viroids, where the latter are infectious, non-protein-coding, highly structured small circular RNAs that replicate autonomously and induce diseases in plants.
- Virions can affect all organisms, while viroids can only affect plants.
