Question
Question: Vector \(\overrightarrow A \) which is directed along the x axis, is to be added to vector \(\overri...
Vector A which is directed along the x axis, is to be added to vector B, which has a magnitude of 7.0m. The sum is a third vector that is directed along the y axis, with a magnitude that uses 3.0 times of A . What is the magnitude of A ?
Solution
Now in the given question vector A is parallel to x axis and after adding vector B to vector Awe get a new vector C. Now the vector C is parallel to the Y axis which means these three vectors are perpendicular to each other and we can find the missing sides (value) by using Pythagoras formula.
Formula used:
Pythagoras Formula:
h=p2+b2
Where is the b base, is the p perpendicular and is the h hypotenuse.
Complete step by step answer:
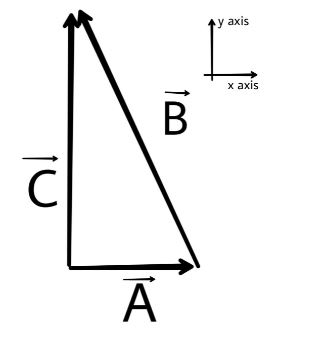
In the given above diagram the vector A is parallel to x-axis and the vector B has magnitude of 7.0m the new vector form is the vector C. In the given question it is given that vector C has a magnitude three times that of vector A.
Let vector A had the magnitude value of =x
So, the magnitude of vector C is =3x
So, we have the base and the perpendicular of a right-angle triangle.The hypotenuse value is:
h=(x)2+(3x)2
⇒h=x2+9x2
⇒h=10x2
Hypotenuse is the vector B which means it has the value of 7.0m
7=10x2
⇒49=10x2.......(Squaring on both the sides)
⇒x2=1049=4.9
∴x=4.9=2.214
Now the value of x=2.214m
So, the vector A has the value =2.214m.
Note: In this case our vectors are perpendicular to each other so this problem becomes easier, if our vectors were at some angle to each other then we had to use the vector addition formula in order to find the length of the unknown vectors.
C=A2+B2+2ABcosθ
Where Aand Bare the two vectors which are being added to each other and θ is the angle between them. The formula can also be used in order to find out the value of vector A where the angle between the vectors will be 90∘ and the value cosθ=0.
