Question
Question: Using VBT, explain the type of hybridization, geometry and magnetic property of \({{\left[ NiC{{l}_{...
Using VBT, explain the type of hybridization, geometry and magnetic property of [NiCl4]2−.
Solution
Generally valence bond theory (VBT) explains the overlapping of atomic orbitals involved in the formation of the molecule. According to valence bond theory bonds are nothing but weakly coupled orbitals.
Complete step by step answer:
- In the question it is given that to write the hybridization, geometry and magnetic property of [NiCl4]2− .
- The IUPAC name of the compound is tetrachloronickelate (II).
- The central metal atom in the given complex is nickel.
- The atomic number of nickel is 28.
- The electronic configuration of nickel is as follows.
[Ar]3d84s2
- The overlapping of atomic orbitals with chlorine atoms is as follows.
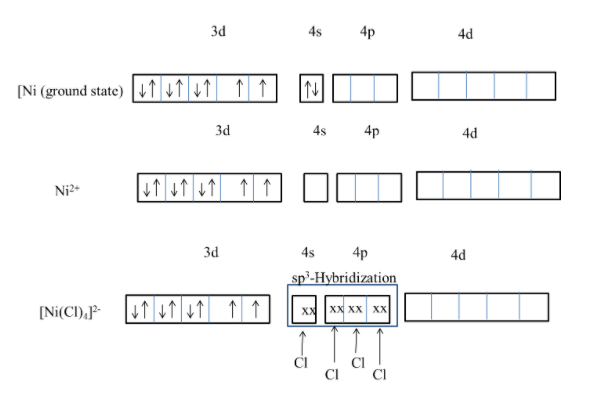
- From the above image we can say that the hybridization of [NiCl4]2− is sp3 .
- The four chlorine atoms donated the electrons to the 4s and 4p orbital of the nickel. This is called overlapping of ligands with the central metal orbitals.
- The geometry of [NiCl4]2− is tetrahedral due to the weak ligand chlorine.
- [NiCl4]2− complex is paramagnetic in nature due to the presence of lone pair of electrons in 3d orbital of the central metal atom nickel.
Note: If the complex has unpaired electrons then it is called paramagnetic and if the complex has no unpaired electrons in the orbitals then the complex is called diamagnetic. Weak field ligands are going to form outer orbital complexes with the central metal atom and strong field ligands are going to form inner orbital complexes with central metal atoms.
