Question
Question: Using the bond enthalpy data given below, calculate the enthalpy change for the reaction (only magni...
Using the bond enthalpy data given below, calculate the enthalpy change for the reaction (only magnitude in nearest integer in kJ/mol),
C2H4(g)+H2(g)→C2H6(g)
| Bond | C−C | C=C | C−H | H−H |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bond energy | 336.81kJ/mol | 606.68kJ/mol | 410.87kJ/mol | 431.79kJ/mol |
Solution
We need to recall the concept of bond enthalpy and understand the bond formation of the given reaction. Bond enthalpy is that which gives the energy to the chemical bond. It is the energy required to break one mole of a chemical bond. Let us consider the bond enthalpy of a single bond between hydrogen and oxygen. The total energy required to break one mole of this bond is 463kJ. We will now study the enthalpy change in the given reaction.
Complete step by step answer:
As we know that when a bond is broken, energy is required and when a bond is created, energy is released. Hence bond breaking is considered to be endothermic and bond creating is considered to be exothermic.
The given reaction is C2H4(g)+H2(g)→C2H6(g) . We can write the skeletal structure of this reaction to understand the breaking and formation of bonds.
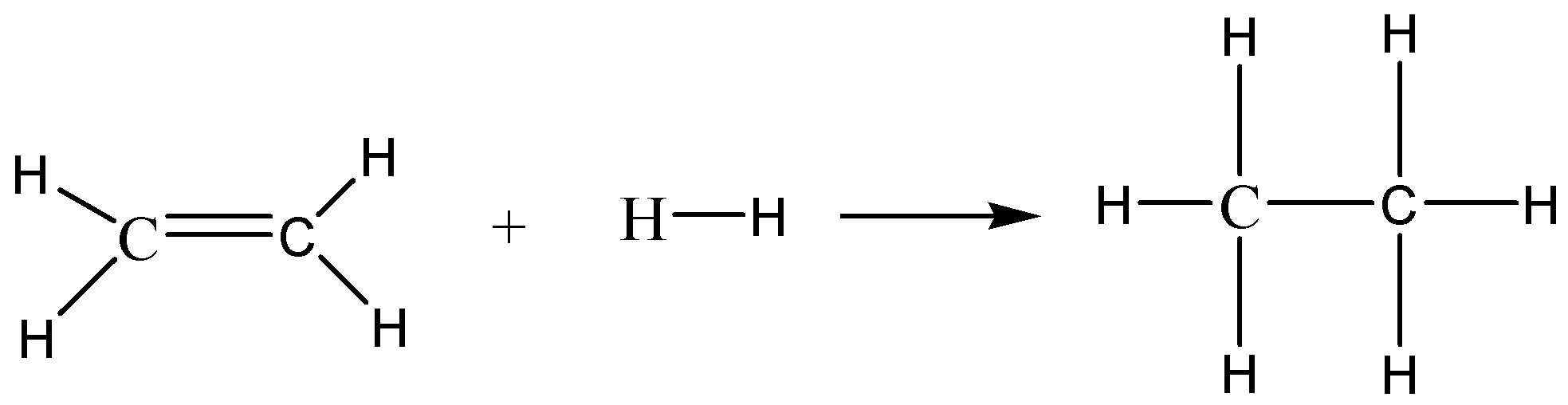
In the reactants: 1C=C bond, 4C−H bonds and 1H−H bond are present.
In the products: 1C−C bond, 6C−H bonds are present.
With the given values of the bond enthalpies of each bond, we can calculate the change is bond enthalpy as follows:
For the reactants: H=606.68+(4×410.87)+431.79= 2681.95kJ/mol
For the products: H=(336.81+6×410.87)= 2802.03kJ/mol
Therefore ΔH=2681.95kJ/mol−2802.03kJ/mol= −120.08kJ/mol
Hence the enthalpy change for the reaction of reduction of ethene to ethane is 120.08kJ/mol(magnitude only).
Note:
It must be noted that the breaking of a chemical bond is always an endothermic process as energy is supplied to break the chemical bonds. Thus, the enthalpy change associated with the breaking of a chemical bond is always positive (ΔH>0). On the other hand, the formation of a chemical bond is almost always an exothermic process. In such cases, the enthalpy change will have a negative value (ΔH<0) . Hence we can say that the conversion of ethene to ethane by reduction is an exothermic process since the enthalpy change is −120.08kJ/mol .
