Question
Question: Using integration, find the area of the region bounded by the triangle whose vertices are (-1,2), (1...
Using integration, find the area of the region bounded by the triangle whose vertices are (-1,2), (1,5) and (3,4).
Solution
Hint : Since we need to integrate and find the area, we must find the equation of the 3 sides of the triangle. For finding the equation of the sides use the two point form of the equation of a line. Then integrate along the x axis.
Formula:
Slope: m=x2−x1y2−y1
Equation of a line when 2 points are given: (y−y2/1)=(x−x2/1).m , where m is the slope of the line.
Complete step by step solution :
The vertices given are (-1,2), (1,5) and (3,4). Let them be A,B and C respectively.
Finding equation of the line AB-
A=(-1,2) and B=(1,5)
Slope= 1−(−1)5−2=23
Taking point B in the equation:
(y−5)= (x−1).23 2(y−5)=3(x−1) 2y−10=3x−3 2y−3x=7......(i)
Equation of line BC-
B=(1,5) and C=(3,4)
Slope= 3−14−5=2−1
Taking point B in the equation:
(y−4)=(x−3)2(−1) 2(y−4)=−(x−3) 2y−8=−x+3 2y+x=11......(ii)
Equation of line AC-
A=(-1,2) and C=(3,4)
Slope= 3−(−1)4−2=42=21
Taking point C in the equation:
(y−4)=(x−3)21 2(y−4)=(x−3) 2y−8=x−3 2y−x=5.....(iii)
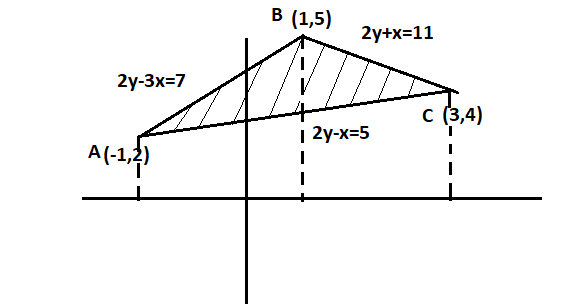
Integrating –
−1∫1AB+1∫3BC−−1∫3AC = area of ΔABC
Since we are integrating along x we find y in terms of x from all the three given equations:
{\text{y = }}\dfrac{{\text{7}}}{{\text{2}}}{\text{ + }}\dfrac{{{\text{3x}}}}{{\text{2}}}{\text{ from}}\left( {\text{i}} \right) \\\
{\text{y = }}\dfrac{{{\text{11}}}}{{\text{2}}}{\text{ - }}\dfrac{{\text{x}}}{{\text{2}}}{\text{ from}}\left( {{\text{ii}}} \right) \\\
{\text{y = }}\dfrac{{\text{5}}}{{\text{2}}}{\text{ + }}\dfrac{{\text{x}}}{{\text{2}}}{\text{ from}}\left( {{\text{iii}}} \right) \\\
=−1∫1[27 + 23x] + 1∫3[211 - 2x] − −1∫3[25 + 2x] =−1∫127 + −1∫123x + 1∫3211 - 1∫32x − −1∫325−−1∫32x =[27x−1]1+[43x2−1]1+[211x1]3−[4x21]3−[25x−1]3−[4x2−1]3 =[27(1)−27(−1)]+[43(1)2−43(−1)2]+ [211(3)−211(1)]−[4(3)2−4(1)2]−[25(3)−25(−1)]−[432−4(−1)2] =[27+27]+[43−43]+[233−211]−[49−41]−[215+25]−[49−41] =7+0+11−2−10−2 =4
The area of the triangle is 4 sq units.
Note : Since we integrated along the x axis the equations were considered in x if we were to integrate along the y axis, the equation would be considered as a whole in y and the limits of integration would be the y coordinates of the triangle.
