Question
Question: Using integration, find the area of the \(\Delta ABC\), the equations of whose sides AB, BC and AC a...
Using integration, find the area of the ΔABC, the equations of whose sides AB, BC and AC are given by y=4x+5,x+y=5 and 4y=x+5 respectively.
Solution
We will start by drawing a rough diagram of the triangle by plotting the given lines and finding their point of intersection. Then we will divide the area into parts as per the graph to find the area of that region with the help of the integration as we know that the area given by integration is algebraic rather than geometric meaning that if the curve is below x-axis then the area will be negative so we have to calculate the area of such parts separately by using integration and add them to find the overall area.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Now, before starting the solution we first to understand that the physical significance of a∫bf(x)dx is,
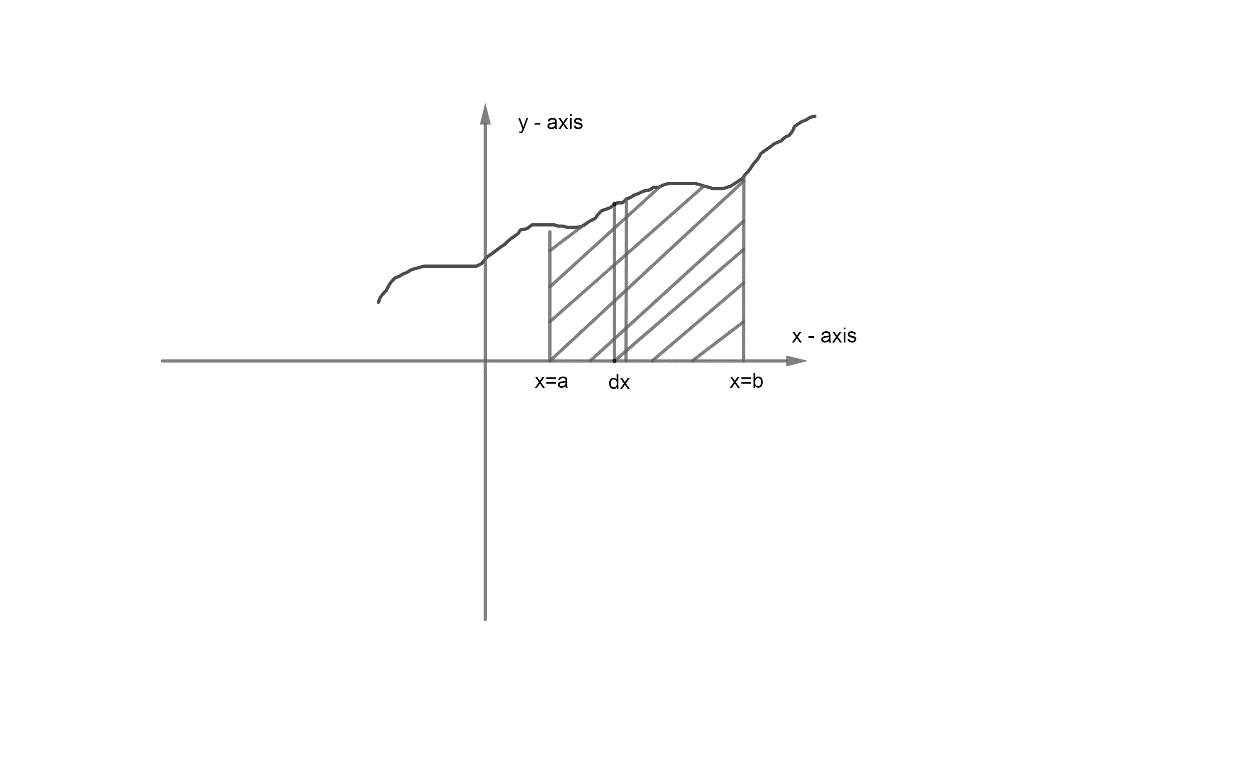
Now, we can see from the graph that a∫bf(x)dx is nothing but the area bounded by the line y=f(x),x=a,x=b and x−axis.
Now, we have the graph of lines y=4x+5,x+y=5 and 4y=x+5 as,
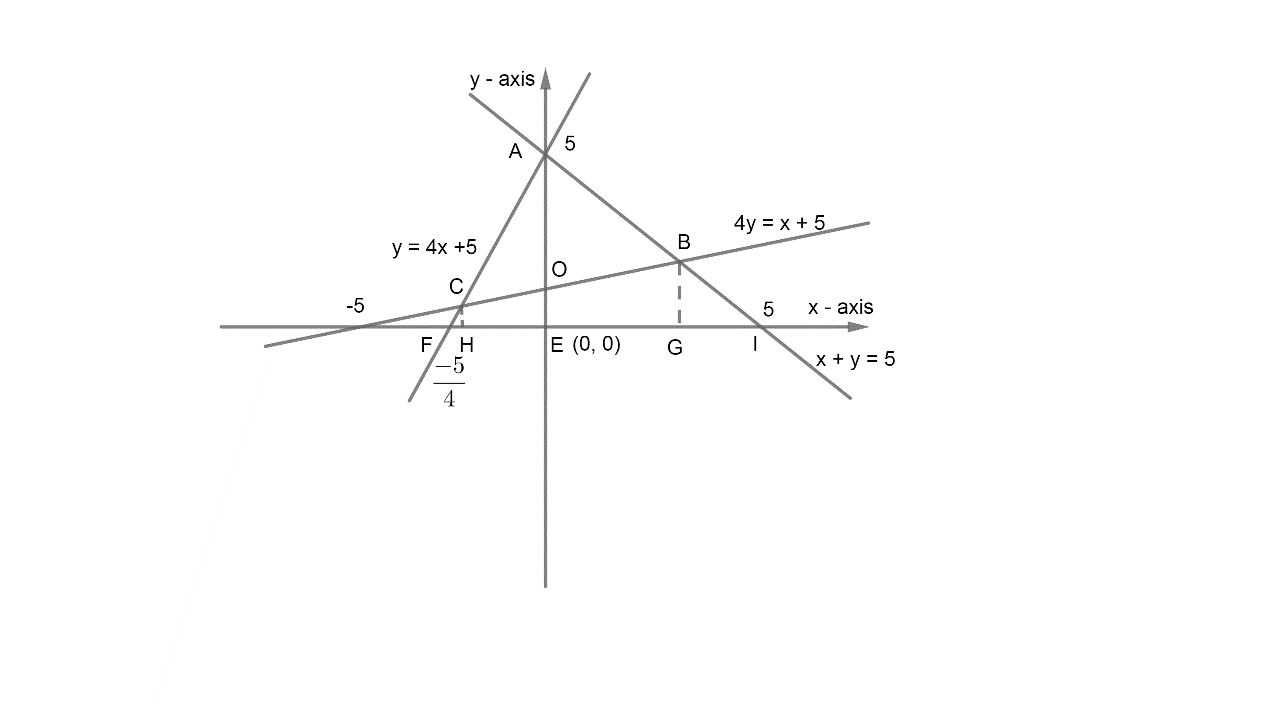
Now, we have the point A as point of intersection of y=4x+5 and x+y=5. So, we have,
5−x=4x+50=5xx=0
Substituting this in x+y=5 we have y = 5 and therefore, the point A is (0, 5).
Now, point B is point of intersection of,
x+y=5.......(1)4y=x+5.......(2)
Now, substituting x=5−y from (1) in (2). We have,
4y=5−y+55y=10y=2
Now, we substitute y = 2 in (1). So, we have x = 5 – 2 = 3. Therefore, the point B is (3, 2).
Now, point C is point of intersection of,
4y=x+5.......(3)y=4x+5.......(4)
So, now we substitute y from (4) in (3).
⇒4(4x+5)=x+5⇒16x+20=x+5⇒15x=−15⇒x=−1
Now, we substitute x=−1 in (4). So,
⇒y=−4+5⇒y=1
Therefore, the point C is (-1, 1).
Now, we will first find the area of ΔACO. So, we can see that,
arΔACO=arΔAFE−arFCOE=arΔAFE−arΔFGH−arCHEO
Now, we have to find the x – coordinate of point H and point O which we can see are same as that of point C and point E respectively as -1, 0. So, we have,
⇒4−5∫0(4x+5)dx−−1∫0(4x+5)dx−4−5∫−1(4x+5)dx
Now, we know that ∫xndx=n+1xn+1. So, we have,
⇒42x2+5x∣4−50−(8x2+45x)−10−(42x2+5x)4−5−1⇒2(4−5)2+5(0+45)−(8−(−1)2+45(0−(−1)))−(2((−1)2−(4−5)2+)+5(−1+45))⇒2(1625)+45×5−(−81+45)−(2(1−1625)+5(45−4))⇒825+425−(810−1)−(2−825+45)⇒825+50−89−(413−825)⇒875−89−(826−25)⇒875−89−81⇒875−10⇒865sq units
Now, similarly we have the area as,
arΔAOE=arΔAEI−arEOBI=arΔAEI−arEOBG−arBGI⇒0∫5(5−x)dx−0∫34x+5dx−3∫5(5−x)dx
Now, we know that the area ∫xndx=n+1xn+1. So, we have,
⇒(5x−2x2)05−41(2x2+5x)03−(5x−2x2)35⇒(5(5−0)−2(25−0))−41(29−0+5(3−0))−(5(5−3)−(225−9))⇒(25−225)−41(29+15)−(10−8)⇒225−41(239)−2⇒225−839−2⇒8100−39−16⇒8100−55⇒845sq units
Therefore, the area of bounded region is,
arΔACO+arΔAOB⇒865+45⇒8110⇒455sq units
Therefore, the area of the bounded region is 455sq units.
Note: While solving the question it is important to note that we have used the x – coordinate of G as limit and since the x – coordinate of G is same as that of B. Therefore, we have used the x – coordinate of B for substituting the limit while finding the area of ΔAOB.
