Question
Question: Using disk or ring method, how do you find the volume of \[y = {x^2} - x,y = 3 - {x^2}\] about \[y =...
Using disk or ring method, how do you find the volume of y=x2−x,y=3−x2 about y=4 ?
Solution
Hint : Here, we find the volume of the given function using the disk methods. The disk method, also known as the method of disks or rings, is a way to calculate the volume of a solid of revolution by taking the sum of cross-sectional areas of infinitesimal thickness of the solid. The volume V of a solid of revolution, V=πa∫b((f(x))2−(g(x))2)dx .
Complete step by step solution:
The given equation of parabola, we have
The region enclosed by the three curve in the below graph,
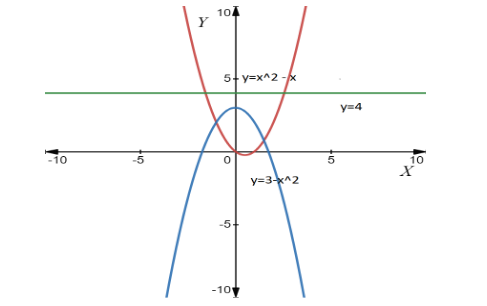
The volume V of a solid of revolution, V=πa∫b((f(x))2−(g(x))2)dx .
Where, V− Volume of solid
a− Least value of x of f(x)
b− Highest value of x of f(x)
f(x)− The value of radius of the disc
dx− The value of height of the disc
To find the point of intersection, where the two parabola meets,
By simplifying the equation to find the point of intersection
2x2−x−3=0 x(2x−1)=3To simplify, we get
x=3 ,
Then, another factor is
The point of intersection, (a,b)=(2,3)
Let the given parabola equation,
To find the volume,
V=πa∫b((f(x))2−(g(x))2)dx
By substituting values in the formula
To simply it by apply the algebraic formula, (a−b)2=a2−2ab+b2
V=π2∫3(((x2)2−2x2⋅x+x2)−(32−2×3⋅x2+(x2)2))dx
V=π2∫3((x4−2x3+x2)−(9−6x2+x4))dx
To evaluate it by using integral, we get
V=π[(5x5−42x4+3x3)−(9x−36x3+5x5)]23
By simplify the above equation, we get
V=π[5x5−42x4+3x3−9x+36x3−5x5]23
Performing addition and subtraction to simplify, we get
V=π[−42x4+37x3−9x]23
Solving the equation by substitute upper and lower limit, we get
V=π[(−42×34+37×33−9×3)−(−42×24+37×23−9×2)]
By simplify the power of the value,
V=π(−42×81+37×27−9×3+42×16−37×8+9×2)
By performing operation for the same denominator value, we get
V=π(4−(2×81)+(2×16)+3(7×27)−(7×8)+9(−3+2))
V=π(42(−81+16)+37(27−8)+9(−1))
Now, we get
V=π(42(−65)+37(19)−9)
Take LCM on above equation, we get
V=π(122(−65)(3)+7(19)(4)−9(12))=π(12−390+532−108)
V=π12(532−498)=π1234=π617
V=617π
Therefore, the volume bounded by the region, V=617π
So, the correct answer is “ V=617π ”.
Note : A solid of revolution is formed by rotating a two-dimensional function around an axis to produce a three-dimensional shape (either a full solid or a ring).Here we use integration to solve the volume bounded by the region with the point of intersection. We remember the formula for volume met by the two parabola functions.
