Question
Question: Two vertices of a triangle are \(\left( 1,3 \right)\) and \(\left( 4,7 \right)\) .The orthocentre li...
Two vertices of a triangle are (1,3) and (4,7) .The orthocentre lies on the line x+y=3 . The locus of the third vertex is:
A. x2−2xy+2y2−3x−4y+36=0
B. 2x2−4xy+3y2−4x−y+42=0
C. 3x2+xy−4y2−2x+24y−40=0
D. x2−4xy+3y2−2x−y+40=0
Solution
Hint : Orthocentre is the point of intersections of perpendiculars drawn from vertex to the opposite side of the triangle.
Equation of line with slope m and passing through (x1,y1) is given as y−y1=m(x−x1) .
Complete step by step solution :
Let PQR be the given triangle and P=(h,k) be the vertex whose locus is to be found.
In the question it is given that the co-ordinates of vertex Q are (1,3) and the co-ordinates of vertex R are (4,7) .
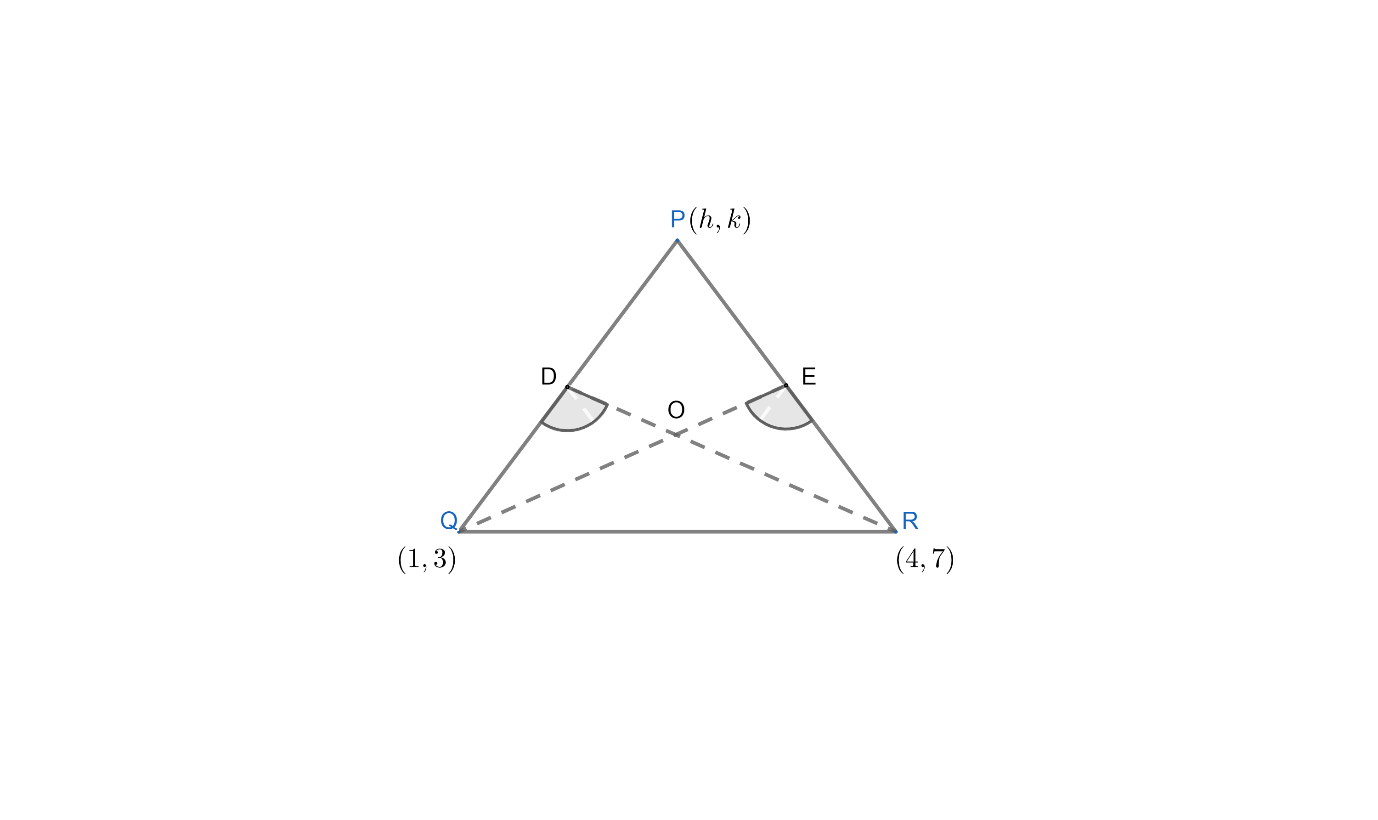
Let the coordinates of the orthocentre be (x1,y1) . Now , from the question we can conclude that (x1,y1) satisfy the equation x+y=3 .
So, x1+y1=3
⇒y1=3−x1
So , the coordinate of the orthocentre becomes (x1,3−x1) .
Now , consider the figure.
Since O is the orthocentre , so RE⊥QE . Now, Q, O and E are collinear. So, the slope of line QE is equal to slope of line QO. Also, R, E and P are collinear. So, slope of RP = slope of RE. RD is perpendicular to QP. R, O and D are collinear. So, slope of RO = slope of RD. Also, Q, D and P are collinear. So, slope of QD = slope of QP.
Now , we know , the slope of the line joining two points (x1,y1) and (x2,y2) is given as m=x2−x1y2−y1.
So, the slope of QE = slope of QO=x1−13−x1−3=1−x1x1 and the slope of RD = slope of RO = 4−x17−(3−x1)=4−x14+x1 .
We know that if two lines are perpendicular to each other , then the product of their slopes is equal to −1 .
So , slope of RE × slope of QE = -1
⇒ Slope of RE ×1−x1x1=−1
⇒ Slope of RE =x1x1−1
Also, QD⊥RD .
So, slope of QD× slope of RD=−1
⇒ Slope of QD ×4−x14+x1=−1
⇒ Slope of QD =x1+4x1−4
Now, let’s find the equation of PE&PD .
We know, equation of line with slope m and passing through (x1,y1) is given as y−y1=m(x−x1) .
So, equation of PE is given as (y−7)=x1x1−1(x−4) .
[We take x1 and y1 as (4,7) because PE passes through R(4,7) .]
⇒x1(y−7)=x1(x−4)−x+4⇒x1(y−x−3)=−(x−4).........(i)
Now, equation of PD is given as (y−3)=x1+4x1−4(x−1) .
[PD passes through Q(1,3) .]
⇒x1(y−3)+4(y−3)=x1(x−1)−4(x−1)⇒x1(y−x−2)=−(4y+4x−16)............(ii)
Now, the vertex P(h,k) satisfies both equations (i)&(ii) .
So, equation (i) becomes x1(k−h−3)=−(h−4).........(iii)
And equation (ii) becomes x1(k−h−2)=−(4k+4h−16).......(iv)
Now, on dividing equation (iii)&(iv) , we get;
x1(k−h−2)x1(k−h−3)=−(4k+4h−16)−(h−4)
⇒(k−h−3)(4k+4h−16)=(h−4)(k−h−2)⇒4k2+4kh−16k−4kh−4h2+16h−12k−12h+48=kh−h2−2h−4k+4h+8⇒4k2−3h2−hk+2h−24k+40=0........(v)
Now, to find the locus of P(h,k) , we will substitute (x,y) in place of (h,k) in equation (v) .
So, the locus of P(h,k) is given as 4y2−3x2−xy+2x−24y+40=0 .
⇒3x2−4y2+xy−2x+24y−40=0
Hence, the locus of P is given by the equation 3x2−4y2+xy−2x+24y−40=0 .
Hence, the correct option is option (c) .
Note : While simplifying the equation take care of sign of terms. These equations can be confusing and sign mistakes are very common. Don’t get confused with orthocenter and circumcentre.
