Question
Physics Question on Ray optics and optical instruments
Two thin convex lenses of focal lengths f1 and f2 are separated by a horizontal distance d (where d < f1, d < f2) and their centers are displaced by a vertical separation Δ as shown in the figure.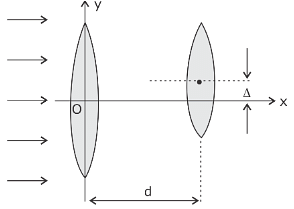 Taking the origin of coordinates, O at the center of the first lens, the x and y-coordinates of the focal point of this lens system, for a parallel beam of rays coming from the left, are given by
Taking the origin of coordinates, O at the center of the first lens, the x and y-coordinates of the focal point of this lens system, for a parallel beam of rays coming from the left, are given by
(A) x=f1f2f1+f2,Y=Δ
(B) x=f1f2+df1+f2-d,Y=Δf1+f2
(C) x=f1f2+df1-df1+f2-d,Y=Δf1-df1+f2-d
(D) x=f1f2+df1-df1+f2-d,Y=0
(C) x=f1f2+df1-df1+f2-d,Y=Δf1-df1+f2-d
Solution
Explanation:
Given:Focal lengths f1 > d and f2 > d Since f1 > d and f2 > d, the focus of both the lenses L1 and L2 lies on the right-hand side of lens L2.The complete ray diagram is shown below: The image formed by L1 will act as a virtual object for the second lens L2.For second lens:Object distance u = f1 - dfocal length = f2Using the lens formula , image distance v is1v-1u=1f⇒1v=1f2+1f1-d⇒v=f2f1-df1+f2-dThe x-coordinate of focal point A of the lens system isx=d+v⇒x=d+f2f1-df1+f2-d⇒x=f1f2+d(f1-d)f1+f2-dThe linear magnification produced by the second lens L ism=vu⇒m=f2f1-df1+f2-df1-d⇒m=f2f1+f2-dThe y- coordinate of the focal point isy=Δ-mΔ⇒y=Δ-f2Δf1+f2-d⇒y=Δf1-df1+f2-dTherefore, the x and y -coordinates of the focal point of the lens system arex=f1f2+df1-df1+f2-d,y=Δf1-df1+f2-d respectivelyHence, the correct option is (C).
The image formed by L1 will act as a virtual object for the second lens L2.For second lens:Object distance u = f1 - dfocal length = f2Using the lens formula , image distance v is1v-1u=1f⇒1v=1f2+1f1-d⇒v=f2f1-df1+f2-dThe x-coordinate of focal point A of the lens system isx=d+v⇒x=d+f2f1-df1+f2-d⇒x=f1f2+d(f1-d)f1+f2-dThe linear magnification produced by the second lens L ism=vu⇒m=f2f1-df1+f2-df1-d⇒m=f2f1+f2-dThe y- coordinate of the focal point isy=Δ-mΔ⇒y=Δ-f2Δf1+f2-d⇒y=Δf1-df1+f2-dTherefore, the x and y -coordinates of the focal point of the lens system arex=f1f2+df1-df1+f2-d,y=Δf1-df1+f2-d respectivelyHence, the correct option is (C).
