Question
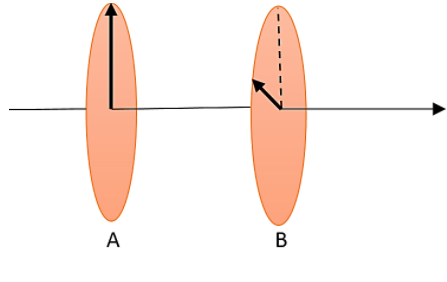
Question: Two Polaroids A and B are placed with their Polaroid axes \(30{}^\circ \) to each other as shown in ...
Two Polaroids A and B are placed with their Polaroid axes 30∘ to each other as shown in the figure. A plane polarised light passes through the Polaroid A and after passing through it, intensity of light becomes I0. What will be the intensity of finally transmitted light after passing through the Polaroid B?
Solution
The intensity I of the transmitted light is changing directly as the square of the cosine of the angle between the analyzer and transmission direction of the polariser. Substitute the angel mentioned in the relation of Malus law.
Formula used:
I=I0cos2θ
Where I be the current intensity, I0 be the initial intensity of the light and θ be the angle between transmission axes and analyzer.
Complete answer:
As we already said, the malus law states that, the intensity I of the transmitted light is changing directly as the square of the cosine of the angle between the analyzer and transmission direction of the polariser.
This can be written in the form of an equation,
I=I0cos2θ
As already mentioned in the question, the angle between the transmission axes and the Polaroid is given as
θ=30∘
Let us substitute this in the equation of malus law,
I=I0cos230
As we all know the value of cosine of 30∘ is written as,
cos30=23
Taking the square of this,
cos230=0.75
Substituting this in the equation will give,
