Question
Question: Two insect species were used in a laboratory experiment. For the treatment, both species were grown ...
Two insect species were used in a laboratory experiment. For the treatment, both species were grown by themselves on a suitable food source. For the second treatment, the two species were grown together on the same type and amount of food as in the first treatment. The given figure shows the results the two species should be classified as.
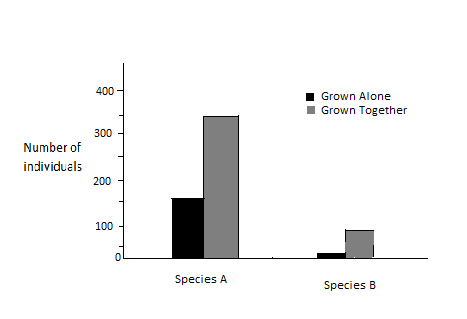
A) Competitors
B) Mutualists
C) Predators or pathogens
D) Commensalism
Solution
They are affected by the conditions in which they live, and by the resources that they obtain but no organism lives in isolation under natural conditions organisms live together influencing each other life directly or indirectly. Members of the biotic community are dependent on one another. The interactions, mainly for food, space, reproduction, and protection. These interactions are important for the survival of different species and the community as a group.
Complete answer:
Competitors:
It occurs when two organisms compete for the same resources (food, space, mates, etc.), resulting in reduced fitness in competing individuals. In the competition between two species both suffer adversely usually, competition occurs when resources, such as space, light, and nutrients, are in short supply. Competition can be interspecies or intraspecific.
Mutualism:
It is a symbiotic relationship between members of two different species in which both members of the association benefited. Based on these relationships, individuals of both species enhance their survival, growth, or reproduction, ritualistic relationships involve diverse interactions. Mutualisms can vary in the degree of dependency between mutualists. Based on this mutualisms can be obligate or facultative. In obligate mutualism, both organisms benefit by living in close association, and the relationship is obligatory. Obligate mutualists cannot survive or reproduce without the ritualistic interaction in facultative mutualism, mutualists benefit by living in the class association, but the relationship is not obligatory.
Predator or pathogens:
The term predation is defined as the consumption of one living organism by another excluding scavengers and decomposers is an act of capturing, killing and eating the organism which does the act of predation is called a predator. The second organism is killed and eaten is called prey. Predation is generally linked to carnivorous animals and the predator is generally larger compared to the prey. Although the term predator is typically associated with animals that feed on other animals, herbivory is also a form of predation in which animals prey on autotrophs.
Commensalism:
It means it is the symbiotic relationship between two species in which one species benefits and the other neither benefits nor is harmed, often. The host species provides a home and transportation for the other species. One very common example of commensalism is epiphytes growing in branches of tropical trees.
Hence, the correct answer is option (B).
Note: Mutualism is the duration of intimacy among mutualistic interactions and also the degree of specificity of mutualistic interactions varies from one interaction to another. The mutualistic interaction can range from one to one, species-specific associations to association with a wide diversity of mutualistic partners. Mutualisms can be subdivided according to the services provided, regardless of whether the participants are obligate or speculative mutualists. According to the nature of service involved, mutualisms can be dispersive, defensive, and resource-based mutualism.
