Question
Question: Two infinite sheets carry equal and opposite uniform charge of densities \(\pm \sigma\). The electri...
Two infinite sheets carry equal and opposite uniform charge of densities ±σ. The electric field in the free space between the two sheets will be:
a). ϵ0σ
b). 2ϵ0σ
c). ϵ02σ
d). Zero
Solution
Hint: Since the two electric plates are oppositely charged and are infinite, we can neglect the fringing effect here and by using the Gauss law, we can calculate the electric field in the free space between the two sheets.
Complete step by step solution:
It has been given that two infinite sheets carry opposite uniform charges of densities +σ and −σ respectively, which we can represent as below
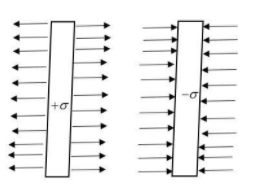
Taking the direction towards right as positive, and by using Gauss law the electric field by a infinitely long charged sheet can be given by E=2ϵ0σ, where σ is the charge density and ϵ0 is the permittivity.
So, the electric field from the sheet with the positive charge density, E’=2ϵ0σ ………. (i)
And electric field due to the sheet with negative charge density,
E’’=−2ϵ0σ ………. (ii)
Now, we need to find the electric field in the space between the two charged sheets,
Therefore, E=E’−E’’=(2ϵ0σ)−(−2ϵ0σ)=ϵ0σ
Hence, option a is the correct answer.
Additional information:
Gauss law states that electric flux through any hypothetical closed surface is always equal to the ϵ01 times of the net electric charge within that closed surface. It is given by the relation
ΦE=ϵ0Q, where Q is the charge in the closed surface and ϵ0 is the permittivity of the medium in which the closed surface is present.
Note: It should be noted that for a positively charged sheet the electric field lines will be in a direction away from the sheet while that of for a negatively charged sheet, its direction will be towards the sheet itself. So, direction should be considered carefully or else we can get ambiguous answers.
