Question
Question: Two diagonally opposite corners of a square loop made of four thin rods of the same material, same d...
Two diagonally opposite corners of a square loop made of four thin rods of the same material, same dimensions are at temperatures 40∘ and 10∘. If the only heat conduction takes place then the temperature difference between the two other corners will be
A. 0∘B. 10∘C. 25∘D. 15∘
Solution
Heat transfer occurs due to the temperature difference, and heat flows from higher temperature to lower temperature. If two heat conducting materials, having the same dimensions, are made of the same materials, then temperature also decreases at the same rate. Heat always transfers from high temperature to low temperature. The heat conduction formula can be used to calculate the heat transfer rate across two points, where thermal conductivity constant (k) depends on the material used.
Formula used:
Rate of heat conduction (H) through a slab is given by
H=ΔxkAΔT
Where,
A is the cross-sectional area of the slab
ΔT is the temperature difference between two points
Δx is the thickness of the slab
K is the proportionality constant, which is called thermal conductivity of the material.
Complete step-by-step answer:
First, we will draw corresponding diagram:
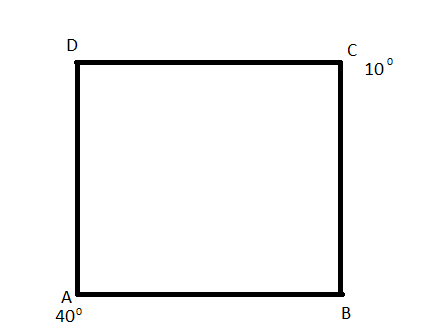
We are asked to find the temperature difference between points B and D, which is TB−TD.
From the above formula, we can say that heat conduction rate (H) is directly proportional to cross sectional area (A) and temperature difference ΔT, and H is inversely proportional to slab’s thickness Δx.
The square loop in the above question is made of the same material, and wire having the same dimensions. So Δx, A and k will not affect calculation and heat will flow at the same rate through all four wires.
Heat flow through path ADC = Heat flow through path ABC
⇒H1=H2
But rate of heat conduction (H) through a slab is given by H=ΔxkAΔT, so the above equation can be written as,
xADkA(TA−TD)=xABkA(TA−TB)
Now we know,
xAD=xAB
So, we get
TB−TD=0
Because heat will flow at the same rate through all four wires, heat will reach point B and point D in the same amount of time. Thus, the temperature difference between B and D will be 0.
So, the answer is A.
Note: Conduction means basically transfer of energy, when one part of a material is heated, it gets excited and transfers energy to its nearest particle, which further transmits the heat energy. Thus, heat energy gets transferred from one end to another. Heat conduction only takes place when there is a difference in temperature between two points.
Heat conductivity differs from material to material. Generally, materials with high heat conductivity are used as sink of heat in mechanical machines.
