Question
Question: Two brands of chocolates are available in packs of 24 and 15 respectively. If I need to buy an equal...
Two brands of chocolates are available in packs of 24 and 15 respectively. If I need to buy an equal number of chocolates of both kinds, what is the least number of boxes of each kind I would need to buy?
A. 2 of first kind, 8 of second kind
B. 5 of first kind, 8 of second kind
C. 5 of first kind, 7 of second kind
D. 2 of first kind, 7 of second kind
Solution
Hint: By prime factorization method take the LCM of the number of chocolates of both brands. To get the least number of boxes, find LCM (24, 15) to the number of chocolate per box.
“Complete step-by-step answer:”
Given the number of chocolate of 1st brand in one pack = 24
The number of chocolate of 2nd brand in one pack = 15
To find the least number of boxes of each kind first we have to find the LCM of 24 and 15.
LCM by prime factorization method.
The method of prime factorization is used to “break down” or express a given number as a product of prime numbers.
The prime number will occur more than once in the prime factorization.
Where the prime number is a whole number which is greater than 1, it is only divisible by 1 and itself.
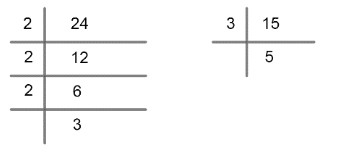
LCM of 24 =2×2×2×3=23×3
LCM of 15 =3×5
LCM of two numbers = product of the greater power of each prime factor involved in the numbers, with highest power.
LCM of 24 =2×2×2××5
LCM of 15 =×5
∴ LCM of 24 and 15 =2×2×2×3×5
LCM (24, 15) = 120
Hence, the number of packet of 1st brand =Number of chocolate in 1st brandLCM (24,15)
=24120=5
Number of packets in 2nd brand =Number of chocolate in 2nd brandLCM (24,15)
=15120=8
∴ 5 of first kind, 8 of second kind
Note: Another way of finding the least number of boxes of both kind,
Number of packet of 1st brand = 24 = 3 x 8
Number of packets in 2nd brand = 15 = 3 x 5
24 = 3 x 8
15 = 3 x 5
∴ 8 of 1stkind and 5 of 2ndkind.
