Question
Question: Two blocks \({M_1}\) and \({M_2}\) is attached to a massless spring as shown in figure. Initially \(...
Two blocks M1 and M2 is attached to a massless spring as shown in figure. Initially M2 is at rest and M1 is moving toward M2 with speed v and collides head-on with M2.
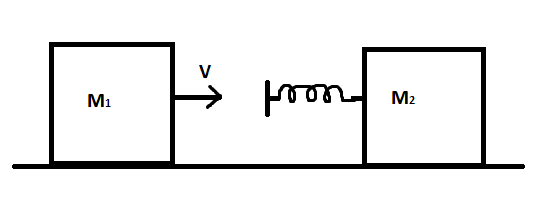
(a) While spring is fully compressed, all the kinetic energy of M1 is stored as potential energy of spring.
(b) While spring is fully compressed the system momentum is not conserved, though final momentum is equal to initial momentum.
(c) If spring is mass less, the final state of the M2 is the state of rest.
(d) If the surface on which blocks are moving has friction, then collision cannot be elastic
Solution
We will be evaluating every option and then conclude which one of the given is followed based upon the given conditions and there reasons to be correct or incorrect.
In elastic collision both momentum and energy is conserved while in inelastic collision neither momentum nor energy is conserved.
Complete step by step answer:
The given figure shows two masses, M2 is at rest while M1 is moving towards it:
Checking the options to conclude which one is true:
(a) While spring is fully compressed, all the kinetic energy of M1 is stored as potential energy of spring:
When M1 comes towards M2 with a certain velocity, it has kinetic energy, some of which gets transferred to the spring as potential energy when it compresses and some of it also transfers to the block of mass M2.
Thus, the given statement stating all the kinetic energy of M1 is stored as potential energy of spring is incorrect.
(b) While spring is fully compressed the system momentum is not conserved, though final momentum is equal to initial momentum:
Momentum of a system is always conserved, be it any kind of collision.
Also, the conserved momentum means initial and final momentum are equal, so the statement too is contradictory to itself.
Thus this statement is also incorrect.
(c) If spring is mass less, the final state of the M2 is state of rest:
This is a special case of collision,
M1 = M2; then the velocities of the bodies get interchanged
M2 was at rest, after collision M1 will be at rest and
M1 was moving with a certain velocity, after collision, M2will acquire that velocity.
So, M1 will be at rest instead of M2 and thus this option is also incorrect.
(d) If the surface on which blocks are moving has friction, then collision cannot be elastic:
If we have friction, then there will always be a loss of energy mostly in the form of heat.
In elastic collision both momentum and energy is conserved while in inelastic collision neither momentum nor energy is conserved.
Thus the collision is inelastic and cannot be elastic and this option is correct.
Thus, it can be concluded that among the given options, option (d) is followed.
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note:
According to the law of conservation of energy, energy can neither be created nor destroyed but transformed from one form to another. So when we say that the energy is not conserved, the energy remains unused and gets out in the environment in the form of heat or light and is known as degraded energy.
