Question
Question: Two blocks A and B of masses m and 2m, respectively are connected by a spring of force constant k. T...
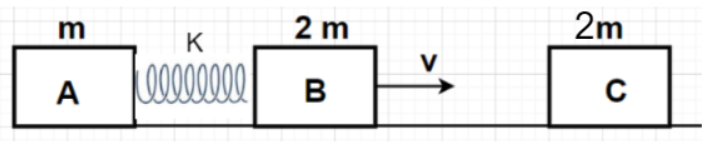
Two blocks A and B of masses m and 2m, respectively are connected by a spring of force constant k. The masses are moving to the right with uniform velocity v each, the heavier mass leading the lighter one. The spring is in the natural length during this motion. Block B collides head-on with a third block C of mass 2m, at rest, the collision is completely inelastic. Calculate the maximum compression of the spring.
Solution
Hint- Here, we will proceed by finding the initial velocity of centre of mass of the complete system. Then, we will apply linear momentum conservation on the system consisting of blocks B and C. Then, we will apply energy conservation to the complete system.
Complete step-by-step solution -
Formulas Used: v0=m1+m2+m3m1v1+m2v2+m3v3, KE = 21mv2 and PE = 21kx2.
Given, Mass of block A = m
Mass of block B = 2m
Mass of block C = 2m
Initial velocity of block A = v
Initial velocity of block B = v
Initial velocity of block C = 0
Force constant of spring = k
As we know that if we have three bodies A, B and C of masses m1,m2 and m3 respectively and having velocities v1,v2 and v3 respectively, then
Velocity of centre of mass of this system (consisting of all these three masses), v0=m1+m2+m3m1v1+m2v2+m3v3
Using the above formula for the given system, we can write
Initial velocity of centre of mass of complete system, v0=m+2m+2mmv+2mv+2m(0)=5m3mv=53v
It is given that complete inelastic collision is occurring between blocks B and C which will lead to sticking of blocks B and C together (i.e., after collision blocks B and C will be moving with the same velocity). Let the final velocity of block B which is equal to the final velocity of block C be v1.
Let us suppose the maximum compression obtained in the spring after the collision be x
Since, the linear momentum (which is equal to the product of mass and velocity) remains same after collision takes place
Consider blocks B and C as a whole system and applying linear momentum conservation, we get
Total linear momentum of blocks B and C before collision = Total linear momentum of blocks B and C after collision
⇒ (Mass of block B)(Initial velocity of block B) = (Mass of block B)(Final velocity of block B) + (Mass of block C)(Final velocity of block C)
⇒(2m)(v)=(2m)(v1)+(2m)(v1) ⇒2mv=2mv1+2mv1 ⇒4mv1=2mv ⇒v1=4m2mv ⇒v1=2v
Final velocity of block B = Final velocity of block C = v1=2v
After collision, block A is moving with initial velocity only i.e., v.
Since, kinetic energy of body having mass m and velocity v is given by KE = 21mv2
Also, potential energy of spring having force constant k and compression x is given by PE = 21kx2
According to Energy conservation, we can write
Total kinetic energy before collision + Potential energy developed in the spring due to compression
= Total kinetic energy after collision
⇒ (Total mass of complete system)( Initial velocity of centre of mass of complete system) + Potential energy developed in the spring due to compression = Kinetic energy of block A + Kinetic equation of block B + Kinetic equation of block C
By substituting v0=53v and v1=2v in the above equation, we get
⇒x2=km[v2−5(53v)2+4(2v)2] ⇒x2=km[v2−5(259v2)+4(4v2)] ⇒x2=km[v2−59v2+v2] ⇒x2=km[2v2−59v2] ⇒x2=km[510v2−9v2] ⇒x2=km[5v2] ⇒x2=5kmv2 ⇒x=5kmv2Therefore, the maximum compression of the spring will be 5kmv2.
Note- In this particular problem, while writing linear momentum conversation between blocks B and C, the linear momentum due to block C before collision is neglected because initially, the block C is at rest (i.e., its velocity is zero) and hence, its contribution for the linear momentum before collision will be zero.
