Question
Question: Two aliphatic aldehydes P and Q react in the presence of aqueous \(\text{ }{{\text{K}}_{\text{2}}}\t...
Two aliphatic aldehydes P and Q react in the presence of aqueous K2CO3 to give compound R, which upon treatment with HCN provides compound S. On acidification and heating gives the product shown below:
The compounds P and Q are respectively:
(A) 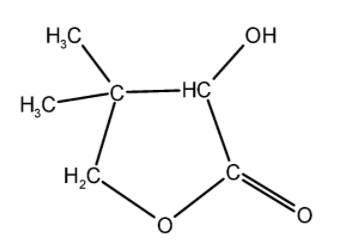
(B) 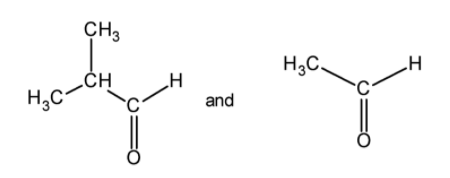
(C) 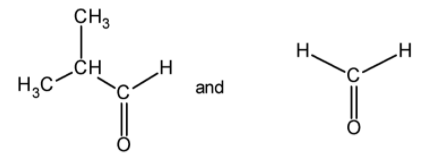
(D) 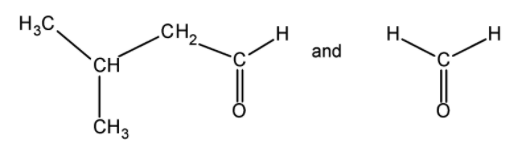
Solution
The aldehydes and ketone which do not contain the α- hydrogen atom undergoes the cross aldol condensation. The condensation results in the hydroxyl aldehyde compound. This method is useful over the self-condensation as we can use two different carbonyl compounds which may or may not have α- hydrogen atom. The reaction of carbonyl compounds with the hydrogen cyanide results in cyanohydrins, which have very wide application in the preparation of carboxylic acid.
Complete answer:
Aldehydes and ketones undergo the condensation in presence of dilute alkali to form hydroxyl aldehyde. The condensation of two different carbonyl compounds (two aldehydes, two ketones or one aldehyde one ketone) in presence of base is called the cross aldol condensation or mixed aldol condensation reaction.
Cross aldol condensation is very useful when the carbonyl compounds do not contain the α- hydrogen atom.
Let’s consider two aldehydes which are 2, methyl propionaldehyde CH3CH(CH3)CHO and formaldehyde HCHO .These aldehydes are different and instead of self-condensation they condense via cross aldol condensation.
Step 1) The base ( K2CO3 or LDA ) abstracts a proton from the 2, methyl propionaldehyde and generates a kinetic enolate .The formation of enolate is as shown below,
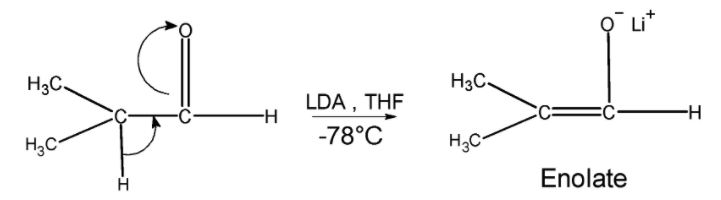
Step 2) this enolate ion formed now attacks on the carbon atom of the carbonyl of the formaldehyde .The attack is as shown below followed by the hydrolysis. This step results in the formation of 3-hydroxy -2, 2 dimethyl propanal.
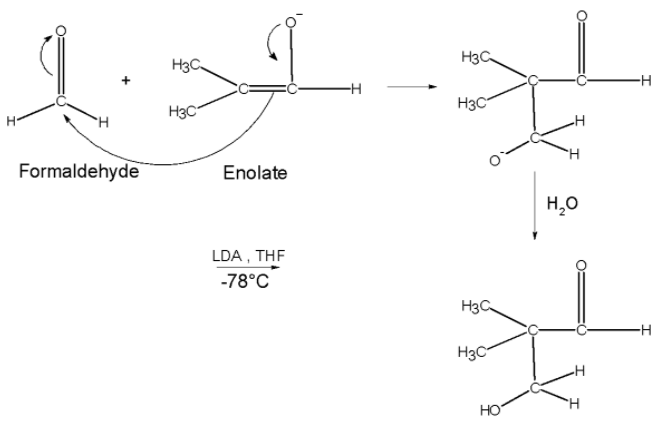
Step 3) the cross aldol product 3, hydroxyl-2, 2 dimethylpropanal is treated with the hydrogen cyanide HCN .Both aldehyde and ketone when added with the HCN and form addition product known as the cyanohydrins. Here, the cyanohydrin of the propanal is as follows,
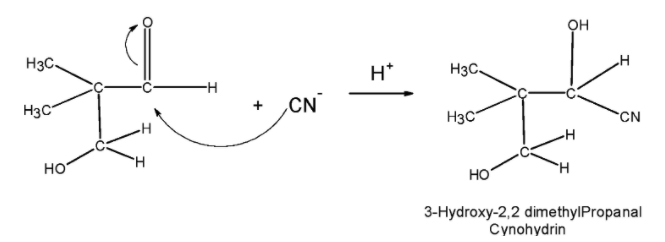
Step 4) The cyanohydrin produced is then treated with the acid such that the cyno group is converted into the carbonyl group .On heating this hydroxyl group abstract a proton from the existing adjacent carbon atom followed by the ring closing. This gives the desired product. The reaction can be given as follows,
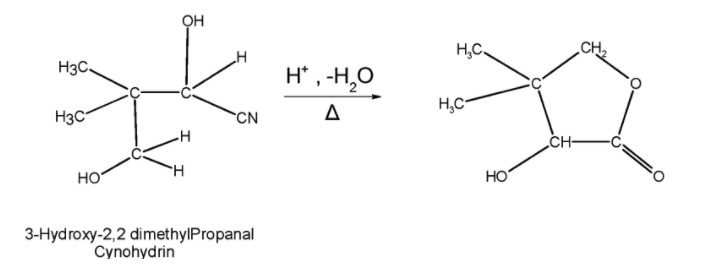
Thus, we obtained the desired product.
Therefore, P is 2-methylpropanal and Q is formaldehyde.
Hence, (B) is the correct option.
Note:
It may be noted that in cross aldol condensation one of the reactants forms an enolate ion and other is more likely to react with it. The reaction is not an aldol condensation as the two same aldehydes are not used .Moreover, the molecules do not have the alpha-hydrogen atom.
Note that addition of HCN is a very slow process; this reaction is carried out in the presence of a base catalyst which acts as a catalyst.
