Question
Question: Three identical metallic uncharged spheres \[A,{\text{ }}B,{\text{ }}and{\text{ }}C\] each of the ra...
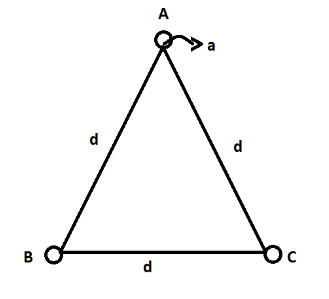
Three identical metallic uncharged spheres A, B, and C each of the radius a, kept at the corners of an equilateral triangle of side d(d≫a) as shown in the figure. The fourth sphere (of radiusa), which has a change inq, touches A and then moves to a position far away. Bis earthed and then the earth connection is removed C is then earthed. The charge on C is:
(A) 2dqa(2d2d−a)
(B) 2dqa(d2d−a)
(C) −2dqa(dd−a)
(D) 2dqa(2dd−a)
Solution
If a charged metallic sphere contacts the same size of metallic sphere, then half of the charge is transferred to another one.If a metallic sphere is earthed, then the net potential on that sphere has become zero. There is a charge dislocation in the earthed sphere by the influence of other charges nearby.
Complete step by step answer:
Initially, there are no charges in A, B, C, spheres. So-net charge qnet=0
Then there is a fourth sphere comes in contact with sphere A
So the charge is transferred to A by an amount of q/2
qA=q/2
Then removed the fourth sphere and earthed the B sphere. (Indicates figure B)
Because of earthed net Potential at B, Vnet=0 and there is a charge q′ on B.
Vnet=VA+VB
Vnet=rAkqA+rBkqB
rA Distance between centre of the sphere A and centre of the sphere B, rA=a+d+a=d+2a but d≫a so rA=d+2a=d.
VA Is the potential due to the sphere A.
VB Is the potential due to the charge dislocation in B.
k is a constant.
Vnet=dk(q/2)+akq′=0
2dkq=a−kq′, then q′=2d−qathis is the charge on B.
Now, earth connection removed from B and earthed C
So, net potential on C =0 Vnet′=0
Vnet′=VA+VB+VC=0
We already know VAand VB and substitute values.
0=2dkq+2d2−kqa+akqC′
Cancel all k
2dkq+2d2−kqa=−akqC′
2dq+2d2−qa=−aqC′
(2dq+2d2−qa)a=−qC′
The charge on C is
qC′=−2dqa[dd−a]
So the answer is (C) −2dqa(dd−a)
Note: Earthed means is the grounding of the metallic sphere. We should count this term 2a in d+2a, if this d≫a is not given. Earthling is used in electrical appliances to prevent electric shock by providing a path of unwanted charge flow.
