Question
Question: Three elephants A, B and C are moving along a straight line with constant speed in the same directio...
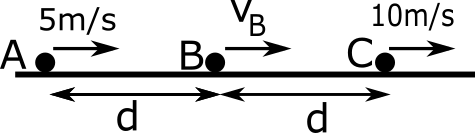
Three elephants A, B and C are moving along a straight line with constant speed in the same direction as shown in figure. Speed of A is 5m/s and speed of C is 10m/s . Initially separation between A and B is d and between B and C is also d .when B catches C separation between A and C becomes 3d. Then the speed of B will be:
A) 15m/s
B) 7.5m/s
C) 20m/s
D) 5m/s
Solution
We can solve this question by using the relative velocity concept. First we calculate what time distance becomes 3d between A and C.
In the same time B catches C it is given then we calculate in what time B catches C and equate the time.
Complete step by step solution:
Step 1
First we calculate in what time separation between A and C become 3d
Elephant A and B having initial separation 2d we assume after time t separation become 3d means separation increased by d this distance d will be travel by elephant C with relative velocity with respect elephant A
Relative velocity of elephant C with respect A is VCA can be given as
⇒VCA=VC−VA
In question given VC=10m/s and VA=5m/s put these in above equation
⇒VCA=10−5 ⇒VCA=5m/s
Hence d distance travel in time t with velocity VCA
We know
velocity=distance x time
⇒VCA=td ⇒5=td
So time
∴t=5d ........ (1)
Step 2
Elephant B catches C in same time in which time separation increase by d between A and C
Elephant B catches C in time t so
Relative velocity of elephant B with respect to C is
⇒VBC=VB−VC
⇒VBC=VB−10
With this relative velocity B travel d distance in time t
Apply velocity=distance x time
⇒VBC=td
⇒VB−10=td
So time
∴t=VB−10d ........ (2)
In question it is given that at the same time B catches C it is given then we calculate in what time B catches C and equate the time.
From equation (1) and (2)
(1)= (2)
⇒5d=VB−10d
Solving this
⇒VB−10=5 ⇒VB=5+10
∴VB=15m/s
Hence velocity of elephant B is 15m/s
Hence option A is correct
Note: Here we use relative velocity concept which can be understand as
VAB=VAG−VBG
Where VAB⇒Relative velocity of A with respect to B
VAG⇒ Velocity of A with respect to ground
VBG⇒ Velocity of B with respect to ground
