Question
Question: Three 60W (120V) light bulbs are connected across a 120V power line shown in figure  light bulbs are connected across a 120V power line shown in figure
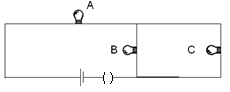
Find
(a) the voltage across each bulb and
(b) the total power dissipated in the three bulbs
A) a) 90 V,40 V, 40 V; (b)40 W
B) a) 80 V,40 V, 40 V; (b)40 W
C) a) 80 V,50 V, 40 V; (b)40 W
D) a) 80 V,40 V, 40 V; (b)50 W
Solution
Hint We need to find the resistance of the bulbs using the ratings of power and voltage provided for the bulbs. Then we have to calculate the net current in the circuit using ohm’s law and then the distribution of voltages across the bulbs.
Formula used: In this solution we will be using the following formula,
⇒P=RV2 where P is the power rating of the bulb, V is the voltage rating, and R is its resistance.
Ohm’s law: V=IR where I is the current flowing through the bulb.
Complete step by step answer
To find the voltage drops across the bulbs, we must first find the current flowing in the circuit for which we need to find the resistance of the bulbs. The resistance of the bulbs can be calculated using the rating of the bulbs which are provided as 60W (120V). Using the relation
⇒P=RV2
We can write
⇒60=R1202
⇒R=240Ω which is the resistance of all the three identical bulbs.
Now B and C bulbs are in parallel and their combination is in series with A. So, the net resistance of B and C is
⇒RBC1=RB1+RC1
⇒RBC1=2401+2401
Which gives us,
⇒RBC=120Ω
The net combination of BC will be in series with A so we have the net resistance as
⇒Rnet=120+240
⇒Rnet=360Ω
The current in the circuit can then be determined using ohm’s law as
⇒I=RV
On substituting the values,
⇒I=360120=31A
Now, when the current flows in the circuit, the current through bulb A will be IA=1/3A but the current will split into two equal parts as their resistance is equal. So IB=1/6A and IC=1/6A .
a) We can now calculate the voltage drop across all the 3 bulbs.
For bulb A, using ohm’s law, VA=IAR
⇒VA=31×240=80V
For bulb B, VB=IBR
⇒VB=61×240=40V
Similarly, for bulb C, VC=ICR
⇒VC=61×240=40V
b) The power dissipated across the bulbs can be calculated using the relation P=I2R
For bulb A: PA=IA2R
⇒PA=91×240=380W
Similarly, for bulb B: PB=361×240
⇒PB=320W
And for bulb C: PC=361×240
⇒PC=320W
Hence the total power dissipated across all the bulbs will be
⇒Ptotal=380+320+320
⇒40W
Hence the correct choice is option (B).
Note
Since bulbs B and C are in parallel, they will have the same voltage drop across them which can help us in eliminating option (C) as the possible answer. While the total current in the circuit will flow across in bulb A since it is connected directly with the battery however for bulbs B and C, the total current will split in half when flowing through those two bulbs.
