Question
Question: Thin, vascular, and folded roof of medulla oblongata is termed as A. Pallium B. Anterior choroi...
Thin, vascular, and folded roof of medulla oblongata is termed as
A. Pallium
B. Anterior choroid plexus
C. Posterior choroid plexus
D. Optic thalami
Solution
The medulla oblongata belongs to the hindbrain and is a pyramid in shape. It receives signals from the spinal cord and transfers to the cerebellum.
Step by step answer:
Pallium – The pallium is the layers of the grey matter and the white matter that cover the upper surface of the cerebrum, in the brains of the vertebrates. It is part of the telencephalon. The cortical part of the pallium in the mammals forms the cerebral cortex.
Anterior choroid plexus – It is the anterior part of the choroid plexus. Anterior choroid plexus is present on the roof of the diencephalon.
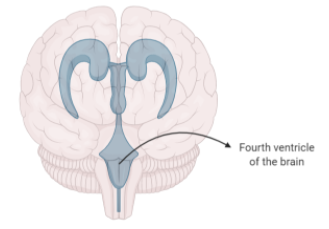
Posterior choroid plexus – The posterior choroid plexus is the roof of the fourth ventricle in the brain that is also known as the metacoel. Hence, the posterior choroid plexus is present on the roof of the medulla oblongata. The choroid plexus in general is a network of the tela choroidea, ependymal cells, and the blood vessels. It has no thick bands of neurons. Due to this reason, it is thin. The blood vessels make the choroid plexus vascularized. The choroid plexus also secretes the cerebrospinal fluid. This fluid protects the brain from the shock by absorbing it. It also keeps the brain moist.
Optic Thalami – The optic thalami are the upper lateral part of the diencephalon that makes up about eighty percent of it. It is the relay center of our brain.
Thus, the thin, vascular, and folded roof of medulla oblongata is termed as the posterior choroid plexus.
Hence, the correct option is (C)
Note: The medulla oblongata is the part of the hindbrain. The hindbrain consists of two parts, namely, metencephalon, and myelencephalon. The myelencephalon includes the medulla oblongata, that controls the general reflex actions, i.e., the involuntary actions since birth. Examples of involuntary actions are the heartbeat, breathing, hiccups, sneezing, yawning, coughing, vomiting, and excretion, etc.
