Question
Question: The work done in dragging a stone of mass \(100 \mathrm{kg}\) up an inclined plane 1 in 100 through ...
The work done in dragging a stone of mass 100kg up an inclined plane 1 in 100 through a distance of 10m is:
(A) 100 J
(B) 980 J
(C) 9800 J
(D) 98 J
Solution
We know that work, in physics, is a measure of energy transfer that occurs when an object is moved over a distance by an external force at least part of which is applied in the direction of the displacement. If the force is being exerted at an angle θ to the displacement, the work done is W=fdcosθ. One joule is defined as the amount of work done when a force of one newton is exerted through a distance of one meter. In the English system of units, where force is measured in pounds, work is measured in a unit called the foot-pound.
Complete step by step answer
We know that work is the measurement of the force on an object that overcomes a resistive force (such as friction or gravity) times the distance the object is moved. When you are doing work against continuous resistive forces, such as gravity or spring tension, work done equals the change in potential energy of the object.
Let us first draw the diagram for better understanding.
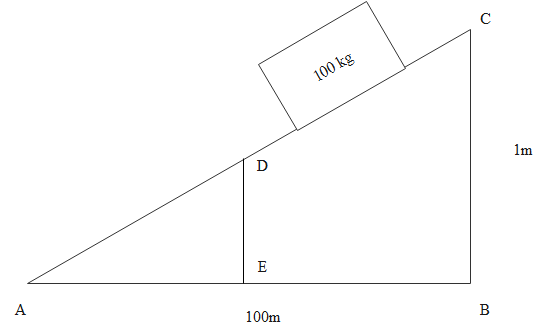
According to the question, AC=1002+12
ACAD=BCDE
So, =1000110
=1DE
We can say that:
=DE≈10010
Hence,
=101
Now we have to find the work done from the required formula.
∴ Work done =mgh
=100×10×.1
=100J
So the correct answer is option A.
Note: We can conclude that work was done with the gravity on a rocket going perpendicular upwards. Zero work: When force and displacement are perpendicular to each other, or when force or displacement is zero. Work done is zero when displacement is zero. This happens when a man pushes a wall. There is no displacement of the wall. Thus, there is no work done. Similarly, when a car is moving on a road, there will be a frictional force applied by the road on the. Work is the energy transferred from an agent applying a force to an object or into heat, and the net work done on an object is the total change of kinetic energy. Both positive work and negative work have meaning: Positive work follows when the force has a component parallel to the displacement.
