Question
Question: The vertices of a triangle are \(A\left( { - 1, - 7} \right)\), \(B\left( {5,1} \right)\) and \(C\le...
The vertices of a triangle are A(−1,−7), B(5,1) and C(1,4). The equation of the angle bisector of the angle ∠ABC is
A) x+7y+2=0
B) x−7y+2=0
C) x−7y−2=0
D) x+7y−2=0
Solution
We know that the angle bisector of an angle of a triangle divides the opposite side in the ratio of the length of the other 2 sides. We can find the distance of the sides of a triangle and find the point of intersection of the bisector with the third side using section formula. Then we can find the equation of the line joining the point of intersection and vertex B. This equation will give the required solution.
Complete step by step solution:
We can draw a triangle with the given vertices. We can draw the angle bisector of the angle ∠ABC and it intersects the opposite side at D.
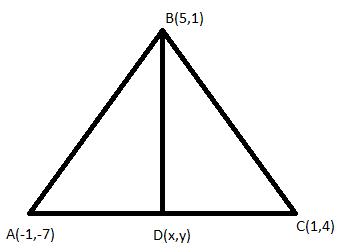
We know that the angle bisector of an angle of a triangle divides the opposite side in the ratio of the length of the other 2 sides.
Now we can find the distance of the other 2 sides.
We know that the distance between to points (x1,y1) and (x2,y2) is given by d=(x1−x2)2+(y1−y2)2
So, the side AB is given by,
AB=(5−(−1))2+(1−(−7))2
On simplification, we get
⇒AB=(6)2+(8)2
On taking the square, we get
⇒AB=36+64
⇒AB=100
On taking the square root, we get
⇒AB=10
Similarly, BC is given by
BC=(5−1)2+(1−4)2
On simplification, we get
⇒BC=42+(−3)2
On taking the squares, we get
⇒BC=16+9
⇒BC=25
On taking the square root, we get
⇒BC=5
So, the ratio is given by,
BCAB=510
So, we have,
⇒BCAB=12
We know that by section formula, the coordinates of the point that divides line joining the points (x1,y1) and (x2,y2) in the ratio m:n is given by, (m+nnx1+mx2,m+nny1+my2).
So, the coordinates of D are given by substituting the coordinates of A and C and the ratio.
⇒D(m+nnx1+mx2,m+nny1+my2)
On substituting the coordinates of A and C and the ratio m:n we get,
⇒D(2+11×(−1)+2×1,2+11×(−7)+2×4)
On simplification, we get
⇒D(3−1+2,3−7+8)
Hence, we have,
⇒D(31,31)
Now we can find the equation of the line joining the points B and D.
We know that the equation of the line joining the points (x1,y1) and (x2,y2) is given by,
y−y1=x2−x1y2−y1(x2−x1)
On substituting the coordinates of the points B and D, we get
⇒y−1=31−531−1(x−5)
On taking LCM, we get
⇒y−1=31−1531−3(x−5)
On cancelling the denominator, we get
⇒y−1=−14−2(x−5)
On simplifying and cross multiplying, we get
⇒7(y−1)=(x−5)
On expanding the brackets, we get
⇒7y−7=x−5
On rearranging, we get
⇒x−7y+2=0
Therefore, the required equation of the angle bisector is x−7y+2=0.
So, the correct answer is option B.
Note:
Alternative solution to the problem is given by,
We know that the angle bisector passes through the angle. So, point B must satisfy the equation of the angle bisector.
Consider option A x+7y+2=0. On substituting the point B(5,1), we get
⇒LHS=5+7×1+2=14=0
So, option A is not a solution.
Consider option B x−7y+2=0. On substituting the point B(5,1), we get
⇒LHS=5−7×1+2=7−7=0
So, option B is the required solution.
