Question
Question: The velocities of two steel balls before impact are shown. If after head on impact the velocity of b...
The velocities of two steel balls before impact are shown. If after head on impact the velocity of ball B is observed to be 3m/s to the right, the coefficient of restitution is:
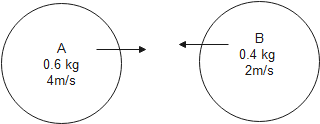
Solution
We know that coefficient of restitution is the ratio between the velocities after collision to that of the velocity before collision. Thus, to find the coefficient of restitution, we need to find the velocities and then use it to find the required answer.
Formula used:
e=velbeforecollisionvelaftercollision
Complete step-by-step answer:
We know that the coefficient of restitution is defined as the ratio between the velocity after collision to that of the velocity before collision. It is given as e=velbeforecollisionvelaftercollision
Here let us consider that the momentum of the balls is conserved, i.e. the momentum before and after collision are equal.
We know that the initial momentum is the sum of the momentum of A and B due to initial velocities.
Let Pi=maua+mbub, and Pf=mava+mbvbwhere, are the masses , is the initial velocities and is the final velocities of of the balls A and B respectively.
We are given the mass and the initial velocity of the balls A and B, then we can say that
Pi=0.6×4+0.4×2
⟹Pi=2.4+0.8
⟹Pi=3.2
Similarly, the final momentum is given as Pf=mava+mbvb, then we have
Pf=0.4×3+0.6×vb,
⟹Pf=1.2+0.6×vb,
If Pi=Pf, we have
⟹3.2=1.2+0.6×vb,
⟹2.0=0.6×vb
∴vb=620
We know that e=velbeforecollisionvelaftercollision
e=UV
Clearly after collision, A and B will move away from each other, thus we have
e=ua+ubva−vb
⟹e=2+42−620
⟹e=6×612−20
⟹e=36−8
∴e=9−2
Thus the coefficient of restitution of the given problem is ∴e=9−2
Note: Here, since we have to find both the final velocity and the coefficient of restitution, we can use the principle of conservation of momentum. Since all the bodies on earth, irrespective of the shape, size or the speed in which they interact, we know that their momentum is conserved.
