Question
Question: The variation of acceleration due to acceleration due to gravity \(g\) with distance \(d\) from Cent...
The variation of acceleration due to acceleration due to gravity g with distance d from Centre of the earth is best represented by (R=Earth’s radius):
A. 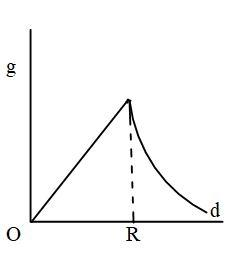
B.
C.
D. 
Solution
The acceleration due to gravity will be different for different conditions; it will vary when measured inside the earth surface, acceleration due to gravity will be different at the surface of the earth and will be different above the surface of the earth.
Formula Used: The acceleration due to gravity inside earth surface is given byg=R3G⋅M⋅r, where G is gravitational constant M is mass of earth R is radius of earth and r is the distance from Centre of earth also R>r and on the surface of earth the acceleration due gravity is given by g=R2G⋅M and out of the earth surface the acceleration due to gravity is given g=r2G⋅M where r is the distance from Centre of earth also R<r, R is radius of earth.
Complete step by step answer:
As the acceleration due to gravity varies at different conditions, so let us see each condition.
When measured inside the surface of earth,
When acceleration due to gravity is measured inside the surface of earth it follows the formula,
g=R3G⋅M⋅r, Where G, M and R are gravitational constant, mass of earth and radius of earth respectively, they are all constants but r is the distance from Centre of earth which can vary. From this relation we can see that g∝r, which means g is proportional to the distance from Centre of earth, therefore the acceleration increases as the distance from the Centre of earth increases linearly. At the surface of the earth acceleration due to gravity varies as g=R2G⋅M, here G, M and R are gravitational constant, mass of earth and radius of earth respectively, they are all constants. Above the surface of earth the acceleration is given by g=r2G⋅M, where G and M is gravitational constant and mass of earth respectively, they are constants but r is the distance from centre of earth which can vary.
Since g∝r21 so we can conclude that till radius of earth the value of acceleration due to constant vary linearly but after that it varies according to the relation g∝r21, so the correct answer is option A.
Note: Students should observe carefully that the acceleration due to gravity varies with the different conditions/distance from the centre of the earth. Inside the earth surface it varies linearly, on the surface of earth it is constant and above the surface of earth it varies according to hyperbola equation.
