Question
Question: The value of \({\sin ^2}\dfrac{{3\pi }}{4} + {\sec ^2}\dfrac{{5\pi }}{3} - {\tan ^2}\dfrac{{2\pi }}{...
The value of sin243π+sec235π−tan232π is
Solution
We have 3 trigonometric functions. We can convert the angles to sum or difference ofπ. Then we can find their values using the equations sin(π−x)=sinx, sec(2π−x)=secxand tan(π−x)=−tanx. Then we can square these values and substitute in the given expression to get the required answer.
Complete step by step answer:
We have the expression sin243π+sec235π−tan232π. We can find the value of each term separately and add them together to get the required value of the expression.
Let us take the 1st term, sin243π.
The angle 43π can be written as π−4π.
⇒sin43π=sin(π−4π)
We know that, sin(π−x)=sinx. Applying this, we get,
⇒sin43π=sin(4π)
We know that sin(4π)=21.
⇒sin43π=21
Taking the square, we get,
⇒sin243π=21 … (1)
Now we can take the 2nd term, sec235π
The angle 35πcan be written as 2π−3π.
⇒sec35π=sec(2π−3π)
We know that, sec(2π−x)=secx
⇒sec35π=sec(3π)
We know that sec(3π)=2
⇒sec35π=2
Taking the square, we get,
⇒sec235π=4 … (2)
Now we can take the 3rd term, tan232π
The angle 32πcan be written as π−3π.
⇒tan32π=tan(π−3π)
We know that,tan(π−x)=−tanx
⇒tan32π=−tan(3π)
We know that tan(3π)=3
⇒tan32π=−3
Taking the square, we get,
⇒tan232π=3 … (3)
On substituting equations (1), (2) and (3) in the given expression, we get,
sin243π+sec235π−tan232π
=21+4−3
=21+1=23
Therefore the value of the given expression is 23
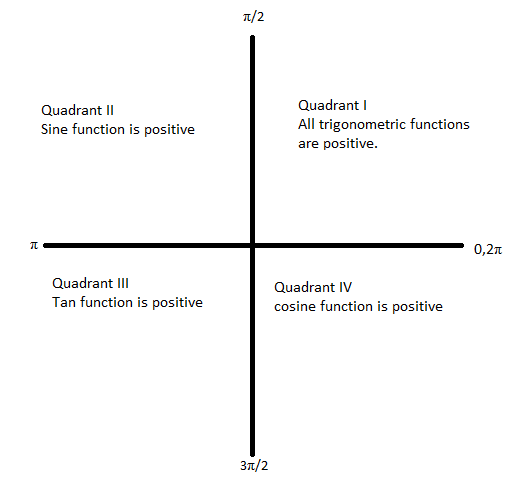
Note: We must know the values of trigonometric functions at common angles. Adding πor multiples of πwith the angle retains the ratio and adding 2πor odd multiples of 2πwill change the ratio. While converting the angles we must take care of the sign of the ratio in its respective quadrant. In the 1st quadrant all the trigonometric ratios are positive. In the 2nd quadrant only sine and sec are positive. In the third quadrant, only tan and cot are positive and in the fourth quadrant, only cos and sec are positive. The following figure gives us an idea about the signs of different trigonometric functions. The angle measured in the counter clockwise direction is taken as positive and angle measured in the clockwise direction is taken as negative.