Question
Question: The V-I characteristics of a silicon diode is shown in the figure. Calculate the resistance of the d...
The V-I characteristics of a silicon diode is shown in the figure. Calculate the resistance of the diode at
(a) ID=15mA and
(b) VD=−10V
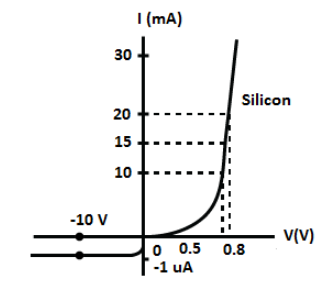
Solution
The inverse of the slope of curve in the V-I graph is the resistance of the diode. Use Ohm’s law to express the resistance of the diode and find the relation between resistance and slope of the curve. For the second part, the change in current is −1μA.
Formula used:
According to Ohm’s law the resistance of the diode is given as,
R=ΔIΔV
Here, ΔV is the potential across the diode and ΔI is the change in the current.
Complete step by step answer:
We have from Ohm’s law the resistance of the diode is given as,
R=ΔIΔV
Here, ΔV is the potential across the diode and ΔI is the change in the current.
Therefore, if we look at the V-I graph of the diode, the resistance is the reciprocal of the slope of the curve. Thus, we can write,
R=m1=I2−I1V2−V1
Here, m is the slope of the curve.
(a) At ID=15mA, let’s find the resistance of the diode as follows,
R=I2−I1V2−V1
Substituting 0.8 for V2, 0.7 for V1, 20 A for I2 and 10 A for I1 in the above equation, we get,
R=(20−10)×10−30.8−0.7
∴R=10Ω
Therefore, the resistance of the diode is 10Ω.
(b) At VD=−10V, let’s find the resistance of the diode as follows,
R=I2−I1V2−V1
Substituting −10V for V2, 0 V for V1, −1μA for I2 and 0 A for I1 in the above equation, we get,
R=(−1−0)×10−6−10−0
∴R=105Ω
Therefore, the resistance of the diode at VD=−10V is105Ω.
Note: In I-V characteristics graph, always denote the voltage along the x-axis and current along the y-axis. The reciprocal of the slope is the resistance of the diode and not the slope of the curve. Note that the resistance of the diode is always the positive quantity.
