Question
Question: The type of isomerism shown by the complex \(\left[ CoC{{l}_{2}}{{\left( en \right)}_{2}} \right]\) ...
The type of isomerism shown by the complex [CoCl2(en)2] is
(A) Ionization isomerism
(B) Geometrical isomerism
(C) Linkage isomerism
(D) Coordination isomerism
Solution
To find the type of isomerism, first, we need to see which type of compounds is given in the question. The types of isomerism are completely different in organic compounds. Here, coordination compounds are given. So, we have to find the type of isomerism accordingly.
Complete step by step solution:
-The given compound is a coordination compound. Such compounds are different from other compounds. They retain their identity in the solution.
-There are basically 2 types of isomerism in such compounds which are structural isomerism and stereoisomerism.
-Structural isomerism is subdivided into ionization, hydrate, linkage, coordination, ligands and polymerization isomerism. Stereoisomerism is subdivided into optical and geometrical isomerism.
-Now looking at the compounds given, we can ensure that the compounds do not have optical isomers as it is not chiral. It has 2 different types of ligands and so can show geometrical isomers of two forms- cis and trans.
-To completely verify the answer, let us eliminate other options. It certainly cannot be ionization isomer as it does not contain any ligands acting as an anion.
Some examples of ionization isomers are [Co(NH3)5SO4]NO3and [Co(NH3)5NO3]SO4
-Linkage isomerism arises when there is a presence of ambidentate ligands like ONO and NO2, SCN and NCS, etc. No ambidentate ion is present. So the isomer is not linkage.
-Coordination isomerism requires the presence of cation and anion group and occurs when they exchange their ligands. No such compounds are present and so this isomer can also not form.
Example of such isomerism is [Cr(NH3)6][Co(CN)6] and [Co(NH3)6][Cr(CN)6] .
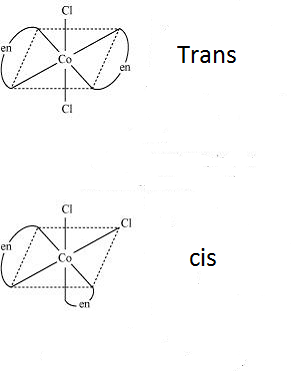
Therefore, the correct option is (B) Geometrical isomerism.
Note: We should know that geometrical isomerism is not possible in tetrahedral compounds as all the 4 different positions are considered to be identical in a tetrahedral structure. Geometrical isomerism occurs in square planar compounds of coordination number 4 and in the compounds with coordination number 6.
