Question
Question: The type of hybridisation and number of lone pair(s) of electrons of Xe in \[XeO{F_{4}}\;\] respecti...
The type of hybridisation and number of lone pair(s) of electrons of Xe in XeOF4 respectively, are:
A.sp3dand 1
B.sp3dand 2
C.sp3d2and 1
D.sp3d2and 2
Solution
To answer this question, you should recall that Xenon is a noble gas and when bonding it will have the tendency to use all the eight electrons in the outermost shell to form bond pairs. We know fluorine is a halogen and can form one sigma bond with the central atom and oxygen can form a double bond with the central atom. Now, use this information to answer the question.
Complete step by step answer:
Hybridization is defined as the concept of mixing two atomic orbitals with the same energy levels to give a degenerated new type of orbitals. This intermixing is based on quantum mechanics. XeOF4has square pyramidal geometry. The central Xeatom has one lone pair electrons and five bonding domains where it donates its outermost eight electrons to four sigma bonded fluorine and one double-bonded oxygen. This results in sp3d2 hybridisation. The geometry or shape is octahedral and the arrangement of electrons around the central atom in the molecule is square pyramidal. The structure can be drawn as:
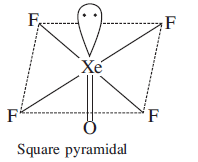
Hence, the correct answer to this question is option C.
Note:
Even if you are not able to calculate the hybridisation using the above-mentioned you can find the hybridization (X) using the formula: 21(V+H−C+A) where
V= Number of valence electrons in the central atom
H= Number of surrounding monovalent atoms
C= Cationic charge
A= Anionic charge. The value of X will determine the hybridisation of the molecule. If Xis 2 then sp; is 3 then sp2 ; is 4 then sp3; is 5 then sp3d ; is 6 then sp3d2 ; is 7 then sp3d3 hybridization.
