Question
Question: The total number of structural isomers possible for a compound with the formula \({{{C}}_{{6}}}{{{H}...
The total number of structural isomers possible for a compound with the formula C6H12, having only one cyclopropane ring, is:
Solution
Isomers are molecules with identical molecular formulas (it means the same type of atoms and the same number of each type of atoms), but a different arrangement of atoms in space. This property of possessing isomers is known as isomerism. Structural isomers are the molecules having the same molecular formula but different arrangements or bonds. For example, butane and isobutene.
Complete step by step answer:
A cyclopropane ring is a ring having three carbon atoms at the corners of a triangle joined together with a single covalent bond and two hydrogen atoms attached to each carbon atom.
The compound having the molecular formula C6H12, having only one cyclopropane ring have six structural isomers. These are
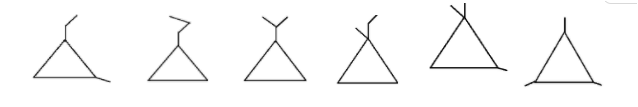
Note: All the isomers have the same molecular formula but have different chemical and physical properties and this is due to the different arrangements of the atoms in the space.
- Structural isomerism is a type of isomerism among many other types of isomerism.
- Structural isomers can be further divided into three types of isomerism are:
- Chain isomers: Chain isomers are the molecules having the same molecular formula but different arrangements of carbon skeleton or the backbone. For example, butane and isobutane.
- Position isomers: These are based on the position of functional groups. These molecules have the same molecular formula and similar functional group but the position of the functional group on the carbon skeleton differs. Example, Butan-1-ol, and Butan-2-ol.
- Functional isomers: these isomers have the same molecular formula but different functional groups. Example: Propanal and Propanone.
- Other than structural isomerism we have stereoisomerism as well. Stereoisomerism or spatial isomerism is a form of isomerism where molecules have the same molecular formula and a similar sequence of bonded atoms but the orientation of atoms in the space is different.
