Question
Question: The \( {\text{Phenol}}\xrightarrow{{{\text{Zn dust}}}}{\text{X}}\xrightarrow[{{\text{anhd}}{\text{. ...
The PhenolZn dustXCH3Clanhd. AlCl3YalkalineKMnO4Z X
Solution
Zn dust plays a role of reducing agent. Here AlCl3 acts as a Lewis acid. Alkaline potassium permanganate acts as an oxidizing agent.
Complete Step by step solution:
Phenol reacts with zinc dust and undergoes reduction to form benzene. This is one of the important processes of preparation of benzene. Phenol first gets converted into phenoxide ion and proton gets released. The proton released will accept an electron from the zinc forming a H radical. As an effect of heating, there is homolytic fission which takes place in the carbon of the phenyl ring and O− .
The O− thus forms an oxide ion. Thus, zinc forms the zinc oxide and the phenyl radical which is produced, forms a bond with H radical. Benzene is formed.
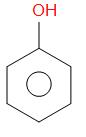 + Zn
+ Zn 
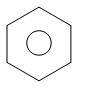 + ZnO
+ ZnO
phenol zinc benzene zinc oxide
The reaction of benzene with anhydrous AlCl3 and CH3Cl is called Friedel-Crafts reaction. Friedel-Crafts reaction proceeds by an electrophilic aromatic substitution.
This reaction proceeds through carbocation rearrangement mechanisms.
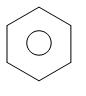
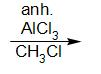
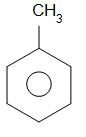
benzene toluene
The product formed is known as toluene.
Alkaline KMnO4 oxidises methyl group that is −CH3 group to the carboxylic acid group which is -COOH group. Hence benzoic acid is obtained as a product.
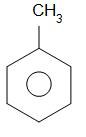
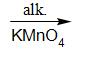
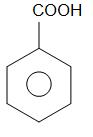
toluene benzoic acid
Therefore, the reaction of phenol with zinc dust gives product X as benzene ring, the reaction of benzene ring with anhydrous aluminium chloride and methyl chloride gives product Y as toluene and the reaction of toluene with alkaline potassium permanganate gives product Z as benzoic acid.
Note:
Benzoic acid that is formed as a product is an aromatic carboxylic acid. Alkaline KMnO4 has a great oxidising power as it provides nascent oxygen. Reducing agents are the reactants which themselves get oxidized and provide hydrogen to other reactants and oxidising agents are the reactants which itself get reduced and provide oxygen to other reactants.
