Question
Question: The tangent of the curve \(y={{x}^{2}}+6\) at a point \(\left( 1,7 \right)\) touches the circle \({{...
The tangent of the curve y=x2+6 at a point (1,7) touches the circle x2+y2+16x+12y+c=0 at Q. Find the coordinates of Q?
Solution
We start solving the by finding the slope of the tangent to the curve y=x2+6 at the point (1,7). We then find the equation of the tangent using the slope that we have just obtained. Using this equation of the tangent, we find the value of c in the equation of the circle given using the fact that the perpendicular distance from center to the tangent in a circle is equal to the radius of the circle. We then substitute the equation of tangent in the circle and make subsequent calculations to get the required coordinates of the circle.
Complete step by step answer:
According to the problem, we have a tangent to the curve y=x2+6 at the point (1,7) touches the circle x2+y2+16x+12y+c=0 at Q. We need to find the coordinates of the point Q.
Let us draw the given information to get a better view.
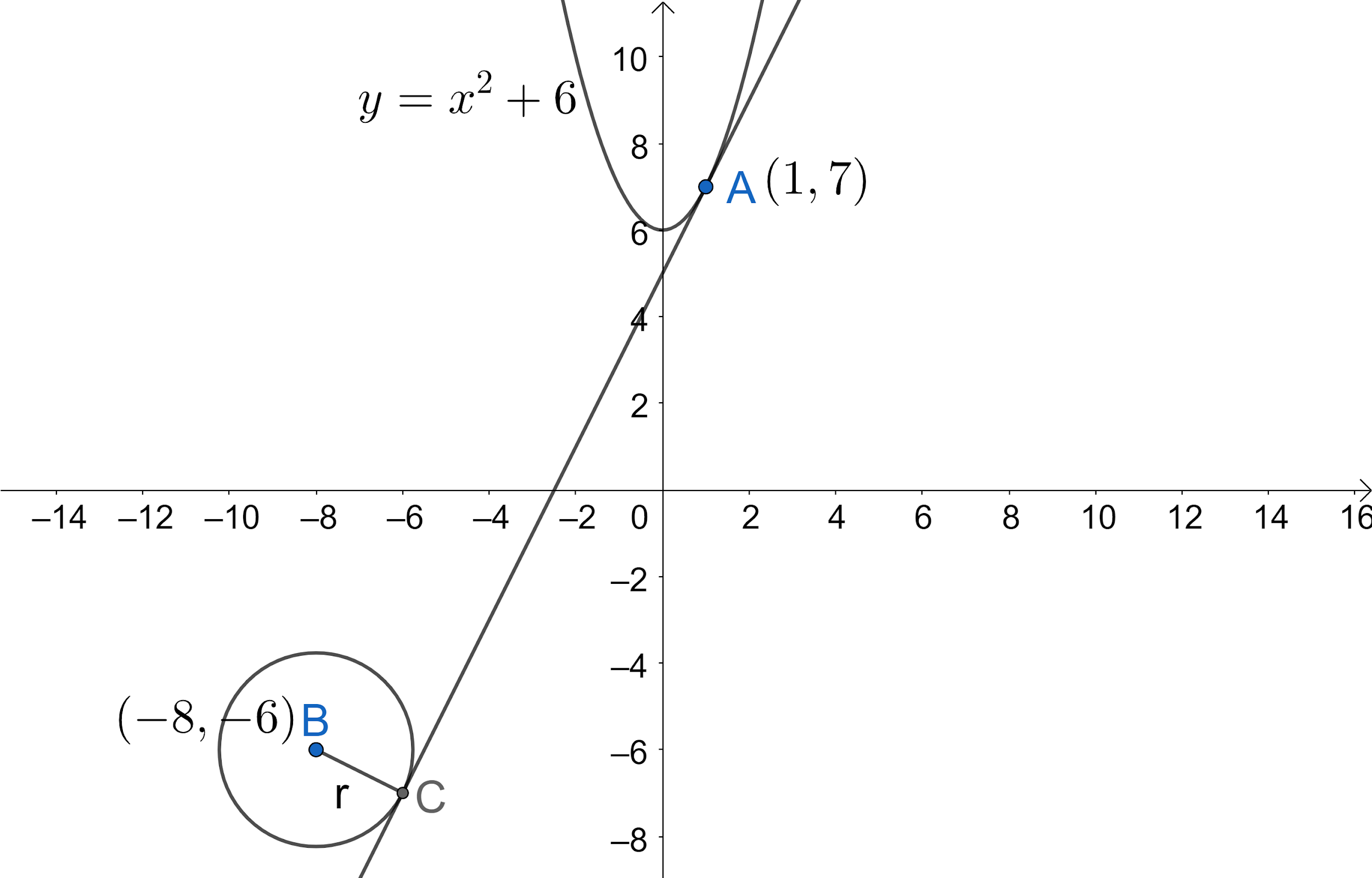
We know that slope of tangent to any curve y at the given point P(x1,y1) is dxdyP(x1,y1).
Let us find the slope of the tangent to the curve y=x2+6 at the point (1,7).
We have y=x2+6. Let us differentiate it with respect to x on both sides.
⇒dxdy=dxd(x2+6).
We know that dxd(f(x)+g(x))=dxd(f(x))+dxd(g(x)).
⇒dxdy=dxd(x2)+dxd(6).
We know that dxd(xn)=nxn−1 and dxd(a)=0.
⇒dxdy=2x+0.
⇒dxdy=2x.
Let us substitute the point (1,7).
⇒dxdy(1,7)=2(1).
⇒dxdy(1,7)=2.
We have got the slope of the tangent to the curve y=x2+6 at the point (1,7) as 2.
Now, we find the equation of the tangent with slope 2 and passing through the point (1,7).
We know that the equation of the line passing through the point (x1,y1) and having slope m is y−y1=m(x−x1).
The equation of the tangent is y−7=2(x−1).
⇒y−7=2x−2.
⇒2x−2−y+7=0.
⇒2x−y+5=0 ---(1).
The equation of the tangent is 2x−y+5=0.
Now, we find the center and radius of the given circle x2+y2+16x+12y+c=0.
⇒x2+16x+64+y2+12y+36−64−36+c=0.
⇒(x+8)2+(y+6)2−100+c=0.
⇒(x+8)2+(y+6)2=100−c.
⇒(x−(−8))2+(y−(−6))2=(100−c)2.
We know that if the equation of the circle is defined as (x−a)2+(y−b)2=r2, then the center and radius of the circle is (a,b) and r.
So, we have got the center and radius of the circle x2+y2+16x+12y+c=0 as (−8,−6) and 100−c ---(2).
We know that the perpendicular distance from center to the tangent in a circle is equal to the radius of the circle.
We know that the perpendicular distance from the point (x1,y1) to the line ax+by+c=0 is a2+b2∣ax1+by1+c∣.
So, we have radius (r) = perpendicular distance from the point (−8,−6) to the tangent 2x−y+5=0.
⇒100−c=22+(−1)2∣2(−8)−(−6)+5∣.
⇒100−c=4+1∣−16+6+5∣.
⇒100−c=5∣−5∣.
⇒100−c=55.
⇒100−c=5.
Now, we square on both sides.
⇒(100−c)2=(5)2.
⇒100−c=5.
⇒100−5=c.
⇒c=95.
So, we got the equation of the circle as x2+y2+16x+12y+95=0 ---(3).
From equation (1), we have the equation of tangent as 2x−y+5=0.
⇒y=2x+5 ---(4).
We substitute equation (4) in equation (3).
⇒x2+(2x+5)2+16x+12(2x+5)+95=0.
⇒x2+4x2+20x+25+16x+24x+60+95=0.
⇒5x2+60x+180=0.
⇒x2+12x+36=0.
⇒(x+6)2=0.
⇒x+6=0.
⇒x=−6 ---(5).
We substitute equation (5) in equation (4).
⇒y=2(−6)+5.
⇒y=−12+5.
⇒y=−7 ---(6).
From (5) and (6), we have coordinates of the Q as (−6,−7).
∴ The coordinates of the Q are (−6,−7).
Note: We can also find the coordinates of the point of contact by finding the point of intersection of tangent 2x−y+5=0 and the line passing through the center of the circle and the point of contact (which is normal here). We should know that the point at which we find the slope lies on both the curve and the tangent. Similarly, we can also expect to find the normal for the given tangent, the point that lies on the opposite side of the diameter which has one endpoint as the point of contact we just obtained.
