Question
Question: The tangent at the point \[\left( {4\cos \phi ,\dfrac{{16}}{{\sqrt {11} }}\sin \phi } \right)\] to t...
The tangent at the point (4cosϕ,1116sinϕ) to the ellipse 16x2+11y2=256 is also a tangent to the circle x2+y2−2x=15. Find the absolute value of ϕ in degrees.
Solution
Here we will first find the equation of the tangent. Then we will find the distance of the tangent from the centre of the circle and equate it with the radius of the circle. Further, we will find the value of cosϕ in this process and hence, the value of ϕ.
Formulas used:
We will use the following formulas:
The tangent to an ellipse with equation a2x2+b2y2=1 at the point (x1,y1) is given by a2xx1+b2yy1=1.
The distance of a point (x1,y1) from a line ax+by+c=0 is given by d=a2+b2∣ax1+by1+c∣.
Complete step by step solution:
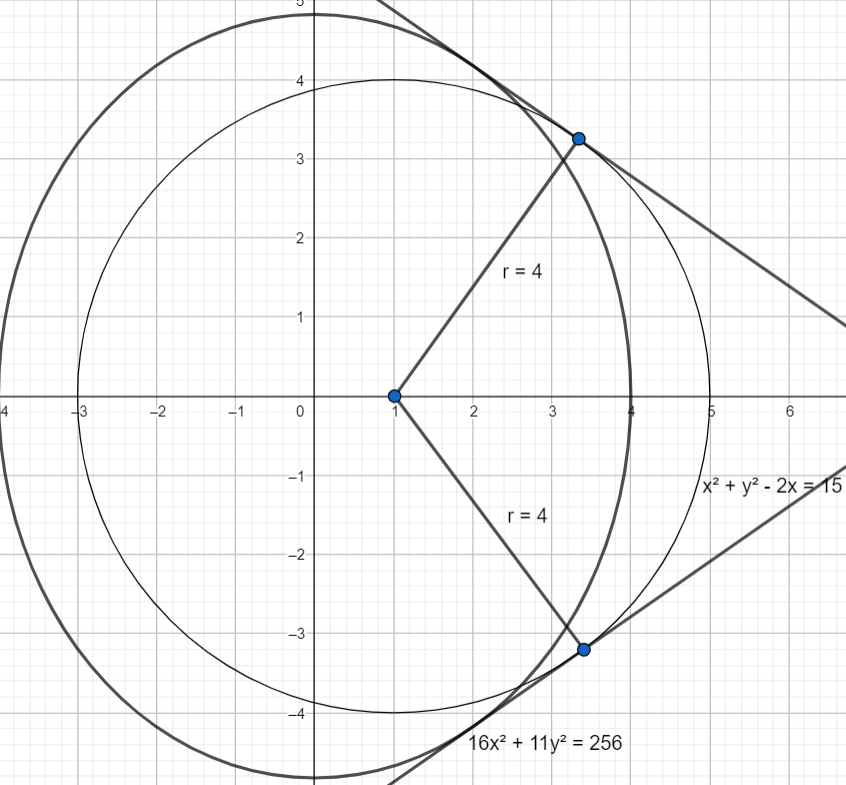
We will write the equation of the ellipse in standard form, a2x2+b2y2=1. We will divide both sides of the equation of ellipse by 256. Therefore, we get
⇒25616x2+25611y2=256256 ⇒16x2+256/11y2=1
Comparing the above equation with a2x2+b2y2=1, we get
a=4
b=1116
The standard form of a circle with centre (h,k) and radius r is given by (x−h)2+(y−k)2=r2.
We will convert the equation of the circle given in the question to standard form. We will add and subtract 1 on the left-hand side of the equation and rearrange the terms, So, we get
⇒x2+y2−2x+1−1=15 ⇒x2−2x+1+y2−1=15
Simplifying the expression, we get
⇒(x−1)2+y2=16
Rewriting the above equation in standard form, we get
⇒(x−1)2+(y−0)2=42……………………(1)
We will compare the above equation with (x−h)2+(y−k)2=r2 and find the centre and radius of the circle. So,
(h,k)=(1,0)=˚4
We will find the equation of the tangent to the ellipse at point (4cosϕ,1116sinϕ) by substituting 4cosϕ for x1, 1116sinϕ for y1, 4 for a and 1116 for b in the formula a2xx1+b2yy1=1. So, we get
⇒16x⋅4cosϕ+11/256y1116sinϕ=1 ⇒4xcosϕ+1611ysinϕ=1
Simplifying the above equation, we get
⇒4xcosϕ+11ysinϕ=16……………………………..(2)
The above line is also a tangent to the circle x2+y2−2x=15.
We know that the distance between the centre of a circle and the point of contact of a tangent is the same as the length of the radius of the circle. We will use this property; we will substitute 4 for d, 4cosϕ for a ,11sinϕ for b, −1 for c, 1 for x1 and 0 for y1 in the formula d=a2+b2∣ax1+by1+c∣.
Therefore we get
⇒4=16cos2ϕ+11sin2ϕ∣4cosϕ−16∣
On cross multiplication, we get
⇒16cos2ϕ+11sin2ϕ=(cosϕ−4)2 ⇒16cos2ϕ+11sin2ϕ=cos2ϕ+16−8cosϕ
Adding and subtracting the like terms, we get
⇒15cos2ϕ+11(1−cos2ϕ)+8cosϕ−16=0 ⇒4cos2ϕ+8cosϕ−5=0
Now factoring the above equation, we get
⇒(2cosϕ+5)(2cosϕ−1)=0
Using zero product property, we get
⇒(2cosϕ+5)=0 ⇒cosϕ=−25
or
⇒(2cosϕ−1)=0 ⇒cosϕ=21
cosϕ cannot be −25 as the minimum value of the function is −1. So cosϕ will be 21.
We know that cos60∘=21.
therefore, the absolute value of ϕ is 60 degrees.
Note:
As cosϕ=21, ϕ can be both 60∘ or −60∘, so there will be 2 tangents that are common to the circle and the ellipse. One of them will have a positive slope and the other will have a negative slope. The concept of tangents is used to find the instantaneous rate of change of a function.
We have used the zero product property to simplify the equation. Zero product property states that if a⋅b=0, then either a=0 or b=0.
