Question
Question: The tangent and the normal lines at the point \(\left( \sqrt{3,}1 \right)\) to the circle \({{x}^{2}...
The tangent and the normal lines at the point (3,1) to the circle x2+y2=4 and the x-axis form a triangle. The area of this triangle (in square units) is:
(a) 31
(b) 34
(c) 31
(d) 32
Solution
The equation of tangent at (3,1) to the circle x2+y2=4 is x−3y−1=[dxdy](3,1). The tangent cuts the x-axis, so we can find the intersecting point of tangent and x-axis by putting y=0.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us draw a circle with centre O(0,0).
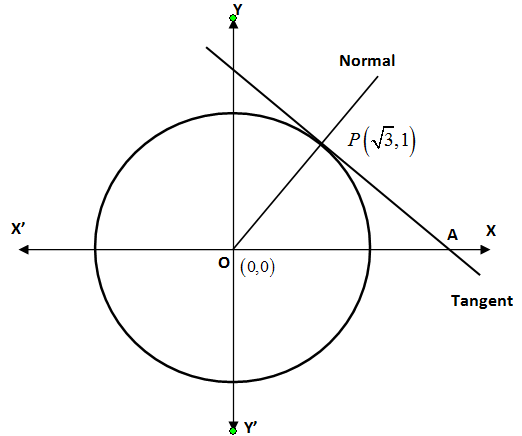
Here you can see that it is given that the tangent and the normal to the circle intersect at a point(3,1). Let us take this point as P(3,1). The tangent will intersect x-axis at point A.
Let us find the equation of the tangent to the circle x2+y2=4. As the tangent meet the circle at pointP(3,1), so first we will find the slope of the tangent at P(3,1).
The slope of the tangent at the point Q(x1,y1) is (dxdy)(x1,y1). Here we have the equation of the circle as x2+y2=4.
If z=xn, then dxdz=nxn−1; and if z=n, dxdz=0, where n is a real number.
Now let us find differentiation of the equation x2+y2=4with respect to x.
Then, 2x2−1+2y2−1dxdy=0
⇒2x+2ydxdy=0
⇒2(x+ydxdy)=0
⇒(x+ydxdy)=0
⇒ydxdy=−x
⇒dxdy=y−x
At point P(3,1), we have x=3 and y=1.
So we have (dxdy)(3,1)=−13=−3.
We know that equation of tangent at point Q(x1,y1) is x−x1y−y1=(dxdy)(x1,y1).
So equation of tangent at point P(3,1) will be
x−3y−1=−3
⇒y−1=−3x+3
⇒3x+y=4 (1)
As the tangent cuts x-axis at A, so at A, y=0. Since the tangent cuts x-axis at A, therefore we shall put y=0in equation (1). Then,
⇒3x+0=4
⇒3x=4
⇒x=34
At point A, x=34and y=0, therefore the coordinate of A is A(34,0).
Now let us find OPand APto find the area of triangle ΔOAP as OP⊥AP. Thus OP is the height of ΔOAP and AP is the base of ΔOAP.
Now,
OP=(3)2+12=3+1=4=2units.
