Question
Question: The sum of real roots of the equation \({{x}^{2}}+5\left| x \right|+6=0\) is A. 5 B. 10 C. -5 ...
The sum of real roots of the equation x2+5∣x∣+6=0 is
A. 5
B. 10
C. -5
D. None of these.
Solution
Hint: Solve for cases when x>0 and x≤0 individually and remove extraneous roots(means which does not satisfy two cases). Use property that |x| = x when x>0 and |x| = -x when x≤0. Find the sum of all the real roots found. Alternatively, you can plot the given function and find the points at which the graph of the given function intersects the x-axis.
“Complete step-by-step answer:”
We will solve the above question for two cases.
Case I: x>0
We have |x| = x
⇒x2+5x+6=0
Using the quadratic formula which states that for quadratic equation ax2+bx+c=0 the roots are x=2a−b±b2−4ac
Here a = 1, b = 5 and c = 6
Using the quadratic formula, we get
x=2(1)−5±52−4(1)(6)⇒x=2−5±25−24⇒x=2−5±1=2−5±1⇒x=2−5+1 or x=2−5−1⇒x=−2 or x=−3
Since x>0 both x = -2 and x = -3 are extraneous roots.
Case II: x≤0
We have |x| = -x
⇒x2−5x+6=0
Here a = 1, b = -5 and c = 6
Using the quadratic formula, we get
x=2(1)−(−5)±(−5)2−4(1)(6)⇒x=25±25−24⇒x=25±1=25±1⇒x=25+1 or x=25−1⇒x=3 or x=2
Since x≤0, both x = 3 and x =2 are extraneous roots.
Hence the given equation has no real roots
Hence option D is correct.
Note: Alternative solution:
If we know the graph of f(x) then the graph of f(|x|) is the same as the graph f(x) for x>0 and for x≤0 the graph is the mirror image taken in the y-axis.
Let f(x)=x2+5x+6
Then f(∣x∣)=x2+5∣x∣+6
First, we draw the graph of f(x)
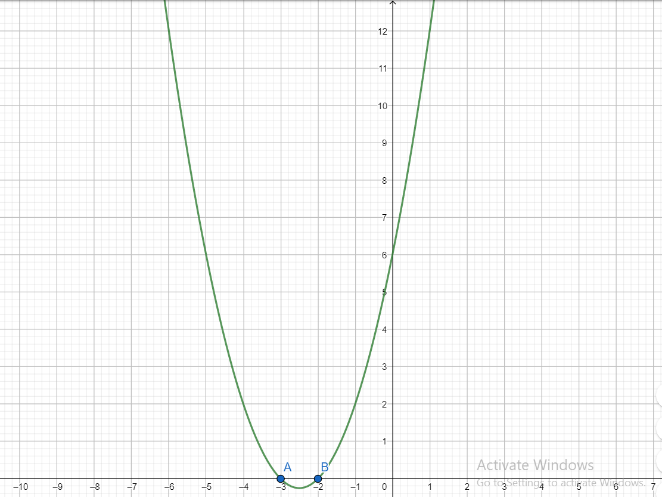
Then using the above-mentioned fact, we draw the graph of f(|x|)
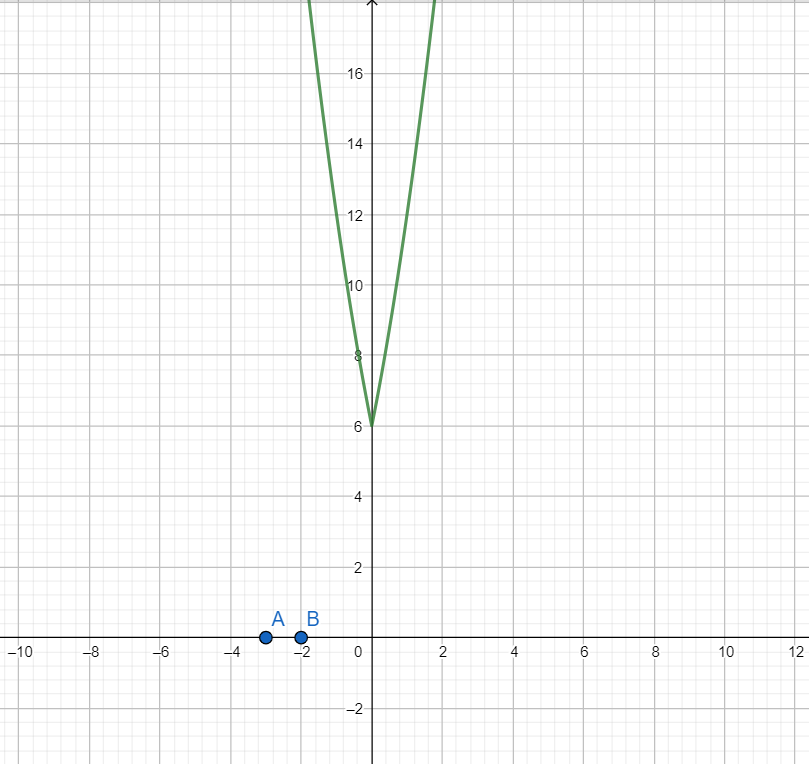
As is evident from the graph, the function f(|x|) does not have any root because it does not intersect the x-axis.
Hence the given equation x2+5∣x∣+6=0 has no real roots.
