Question
Question: The sum of lengths of the hypotenuse and a side of a right angled triangle is given. Show that the a...
The sum of lengths of the hypotenuse and a side of a right angled triangle is given. Show that the area of the triangle is maximum when the angle between them is 60∘?
Solution
Here we will construct a diagram on the basis of given parameters. After that we will find the area of the right angle triangle. Then we will differentiate it with respect to x and find values of maximum value of it. Calculate value of required angle at this value.
Complete step-by-step answer:
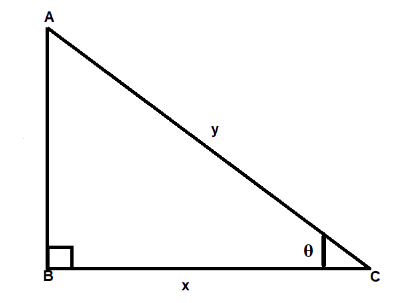
According to the question ΔABC is an right angle triangle, in which BC=x,AC=y
Now we find the value of the side AB by Pythagoras theorem, we get
AC2=AB2+BC2
Now putting the value of BC and AC we get
x2=y2+AB2
By solving this we get,
AB2=x2−y2 AB=x2−y2
Now apply formula of area of right angle triangle
Area=21×BC×AB
Now we put the values in the above formula we get,
Area = 21xy2−x2
Now we square both sides we get,
Area2=4x2(y2−x2)
Now we put y=(k−x), ∵x+y=k(constant) we get
Area2=4x2[(k−x)2−x2]
Now we solve the above equation we apply the formula as (a−b)2=a2+b2−2ab we get
Area2=4x2[k2+x2−2kx−x2]
Now simplifying the equation we get
Area2=4x2[k2−2kx]
Now multiply the numerator by x2 we get
Area2=4k2x2−2kx3 ⋅⋅⋅(i)
Now On differentiating(i), We get
2Area.dxdA=42k2x−6kx2 ⋅⋅⋅(ii)
After simplifying the above equation we get
dxdA=4Ak2x−3kx2
Now, as we know that
⇒dxdA=0 we put the value ofdxdA, ⇒(k2x−3kx2)=0 after simplifying we get ⇒x=3k
Here we are neglecting x=0
Thus, A is maximum when x=3k
Now, we put the value of x in the equation y=(k−x) we get
⇒y=(k−3k) y=(32k)
Now cosθ=ACBC, putting the value we get
∴yx=cosθ
Now we put the value of x, y we get
⇒cosθ=(32k)(3k) ⇒cosθ=21
Hence the value of
⇒θ=3π
Hence, the area is maximum when θ=60∘
Note: Here we can apply differentiation for finding the value of maxima, because we know that maximum is obtained when differentiation will be negative .So for that we have to find differentiation to make it equal zero and get maximum value.
