Question
Question: The structure of orthophosphoric acid is: A. 
B. 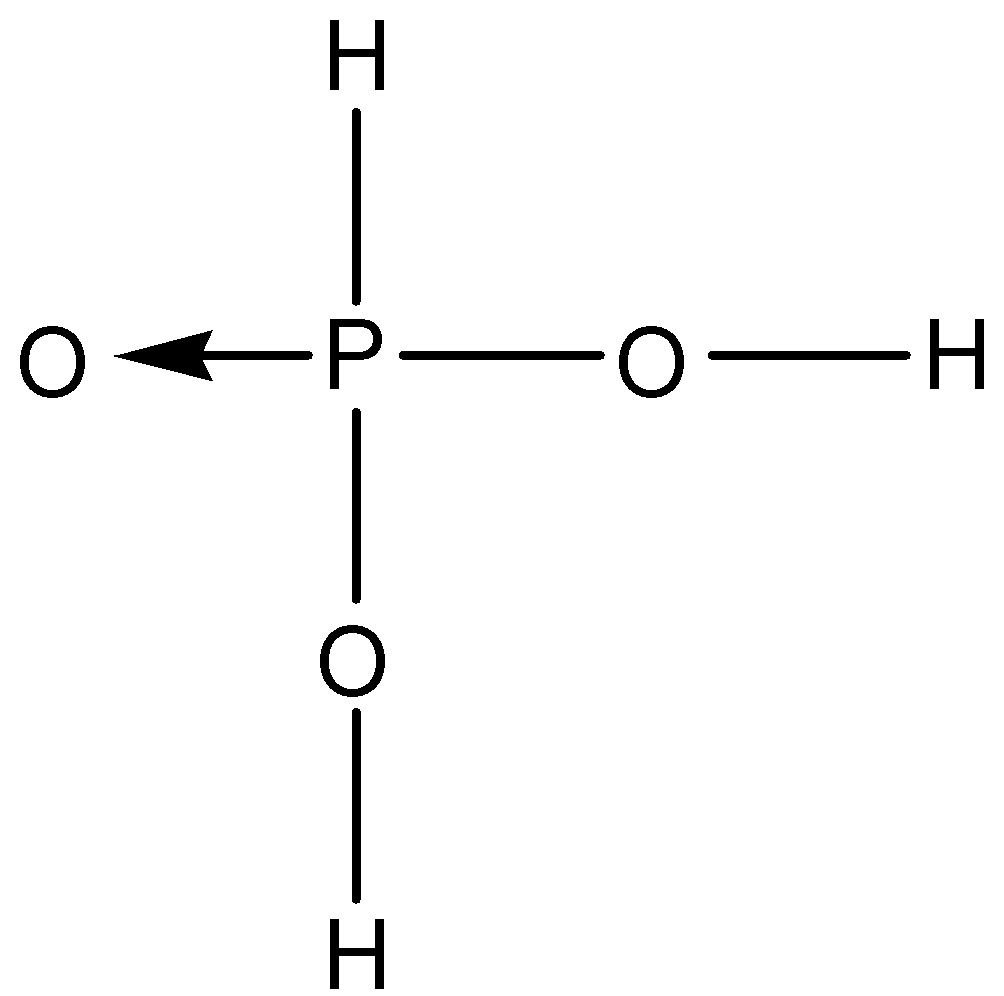
C. 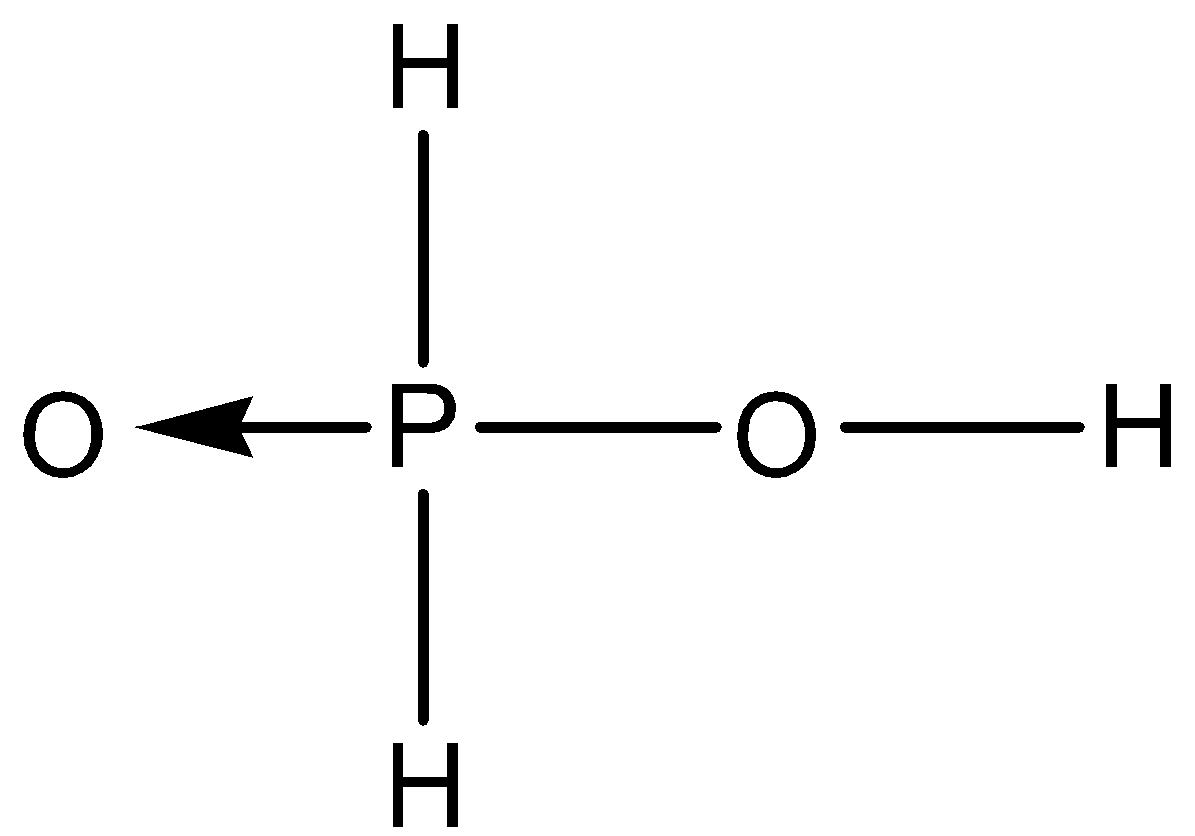
D. 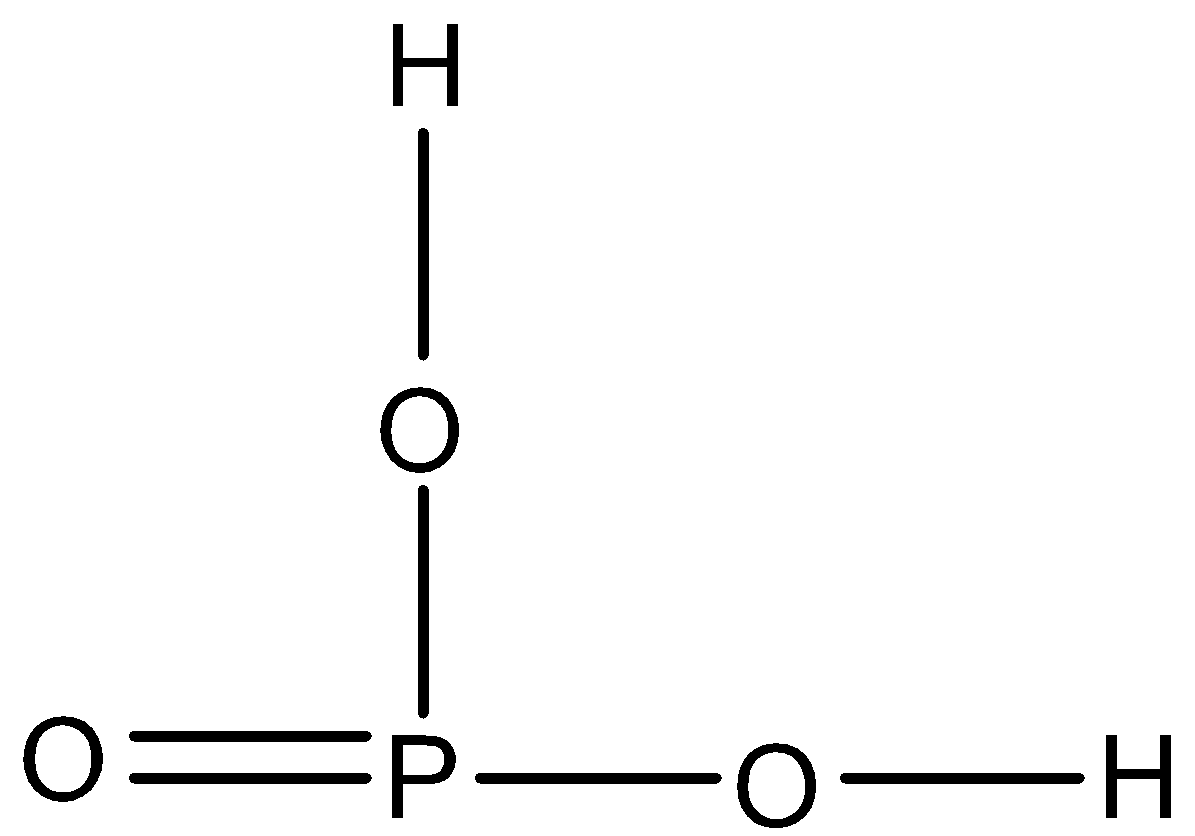
Solution
Think about the chemical formula of orthophosphoric acid, this will help you narrow down the options. Also consider the valency of phosphorus and the acidity of the orthophosphoric acid.
Complete step by step answer:
Orthophosphoric acid is considered to be a weak acid that has the molecular formula H3PO4. Now, let us try to deduce the structure of this acid. We know that the valency of phosphorus is 5, this means that it can form five bonds with neighbouring atoms. One of them is usually a double bond since phosphorus donates a lone pair to form the bond. The only atom that can form a double bond besides phosphorus in H3PO4 is oxygen. So, one phosphorus-oxygen double bond is present. This can also be called a coordinate covalent bond.
Now, onto the other oxygen and hydrogen atoms, phosphorus can still bond with 3 different atoms. We know that orthophosphoric acid is a tribasic acid, this means that it can donate three acidic protons. If any of the hydrogen is bonded directly to the phosphorus atom, it will not be an acidic proton. So, the phosphorus atom is bonded to three oxygen atoms through single bonds and these oxygen atoms are further bonded to three hydrogen atoms. So, the correct structure of orthophosphoric acid is:
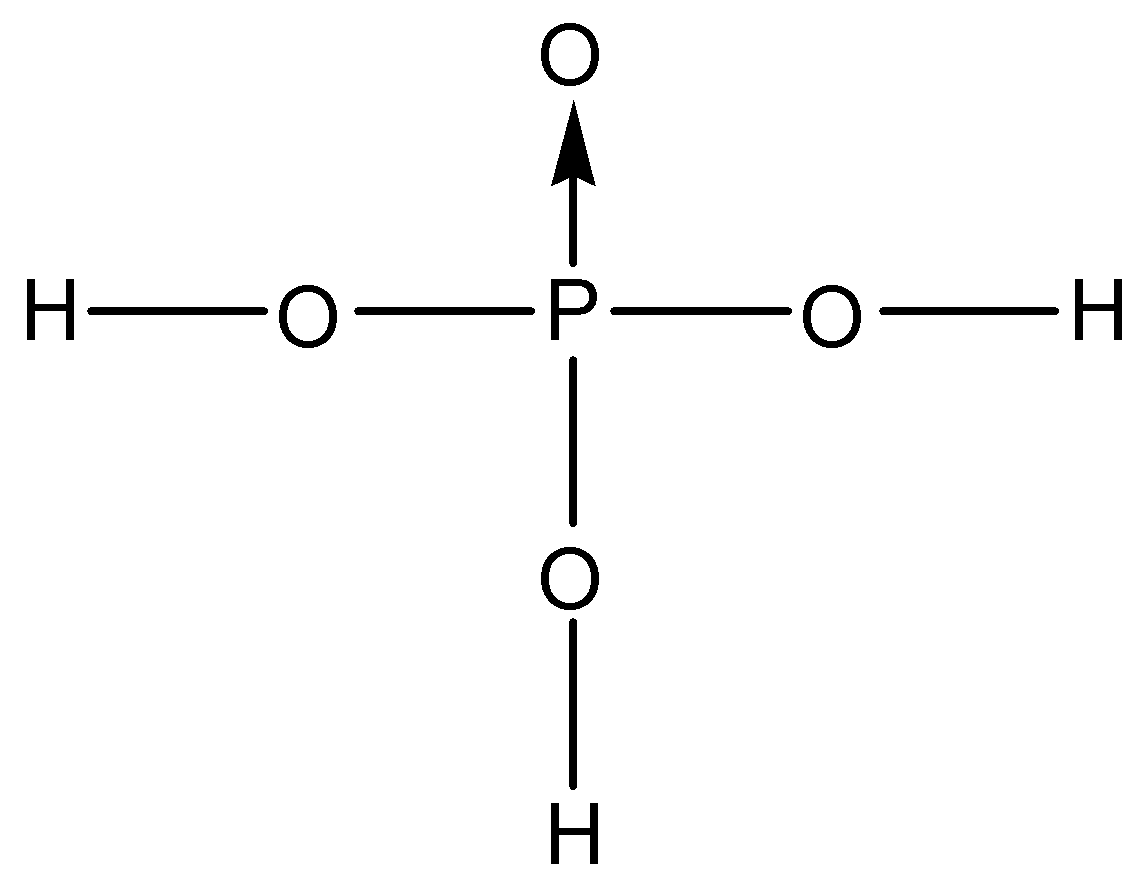
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: A conjugate covalent bond is shown by an arrow. It is shown when the two electrons that are required to form a bond are donated by only one of the atoms that are involved in the bond. The arrow head points towards the receiver of the electrons. Sometimes, these bonds are also denoted as double bonds since two electrons are let out by the same atom.
