Question
Question: The structure of compound B is: \(C{{H}_{3}}CHO+HCHO\xrightarrow[Dil.NaOH]{Heat}\,A\xrightarrow[HCN]...
The structure of compound B is: CH3CHO+HCHOHeatDil.NaOHAH3O+HCNB
(A)- CH3−CH(OH)−COOH
(B)- CH2=CH−CH(CN)−OH
(C)- CH3CH2−CH(OH)−COOH
(D)- CH2=CH−CH(OH)−COOH
Solution
The presence of an aldehyde with α-hydrogen, in presence of a base shows aldol condensation to form an unsaturated carbonyl compound. Also, the cyanide acts as a nucleophile, undergoing addition to the carbonyl compound, followed by the addition of water which converts it into carboxylic acid.
Complete Solution :
In the given reaction, both the reactants are aldehyde, that is, acetaldehyde and formaldehyde. There is a presence of α- hydrogen in the acetaldehyde. So, in presence of the sodium hydroxide base, it undergoes cross aldol condensation with the formaldehyde.
In the aldol condensation, the acetaldehyde loses a proton to the sodium hydroxide base, forming an enolate, which attacks on the carbonyl carbon of the formaldehyde to form the aldol.
Then, the aldol formed on being heated, loses a water molecule to form an α,β− unsaturated carbonyl compound.
The reaction takes place as follows:
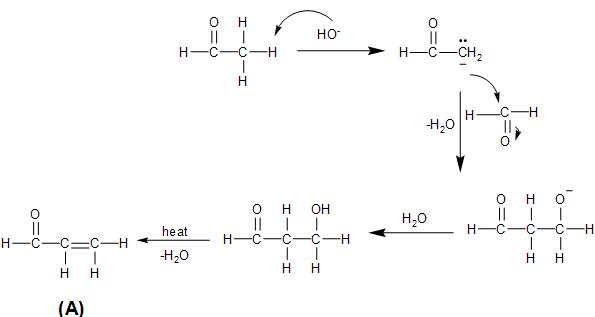
The unsaturated carbonyl compound, prop-2-enal formed above, on reaction with hydrogen cyanide undergoes nucleophilic addition reaction, by the attack of the cyanide ion on the partially positive carbonyl carbon. This is followed by the hydrolysis process which converts the cyano- group to carboxylic group, as follows:
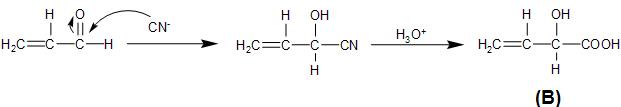
Therefore, the product B, formed from the given reaction step is option (D)- CH2=CH−CH(OH)−COOH.
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note: α- hydrogen is the hydrogen atom present on the adjacent carbon to the carbonyl group, which is present in the acetaldehyde but not in formaldehyde.
Also, a cross aldol condensation reaction takes place due to presence of two different aldehydes in the reaction.
