Question
Question: The structure of \[2 - {\text{Bromo}} - 3 - {\text{ethyl}} - 2 - {\text{methylhexane}}\] ....
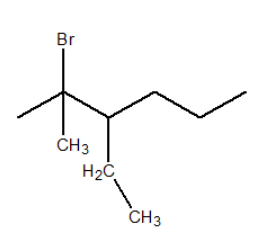
The structure of 2−Bromo−3−ethyl−2−methylhexane .
Solution
A set of rules given by IUPAC is to be followed for naming of the given organic compounds. Also, from the IUPAC name given of organic compounds, its structure can be easily predicted by using the same rules.
Complete step-by-step answer:
IUPAC naming of organic compounds are followed by a set of rules. These rules are as follow as:
Selection of carbon chains. Select the longest carbon chain as the parent chain that contains maximum number of functional groups, multiple bonds and substituent. Priority order is: functional group>multiple bond>substituent . If the main functional group contains carbon, then its carbon should be included in the parental carbon chain. According to the priority table, the highest priority group is called the main functional group while all other lower priority groups are considered as substituent.
Numbering rule. Start the numbering in such a manner that the functional group, multiple bond, and substituent gets the lowest number. Priority order: functional group>multiple bond>substituent . If the main functional group contains carbon then numbering should start from that carbon. In the symmetrical case; when two substituents are present at a symmetrical position, then numbering should be done according to alphabetical order. Double bond gets more priority over triple bond.
If more than one or two substituents are present; then numbering should be done according to minimum number rule or minimum locant rule.
Priority order of functional group is:
carboxylic acid>sulphonic acid>anhydride>ester>acid halide>amide>cyanide>isocyanide>
aldehyde>ketone>alcohol>thio alcohol>amine .
Always use a comma between two numbers. If a functional group, multiple bonds, substituent are present more than one time; then use di, tri, and tetra and so on. In case of radicals; numbering should be done from free valency carbon always.
From 2−Bromo−3−ethyl−2−methylhexane we can suggest that the main carbon chain consist of six carbons and without any double or triple bond at any place. Also the presence of substituent are as follows: Bromine is attached at second carbon, ethyl group is attached at third carbon and methyl group is attached at second carbon of the parent carbon chain. Thus, structure can be given as:
Note: In an organic compound with polyfunctional groups, a principal group must be chosen as per the priority order. The name of this group must be declared by using its suffix name. all other functional groups except the principal group must be declared by using their prefix name in alphabetical order.
