Question
Question: The state of hybridization of the central atom in dimer of \[B{H_3}\] and \[Be{H_2}\] ? A. \[s{p^2...
The state of hybridization of the central atom in dimer of BH3 and BeH2 ?
A. sp2,sp2
B. sp3,sp2
C. sp3,sp3
D. sp2,sp
Solution
First we must know about the valency of the central metal atom in the given compound. Therefore, the Boron is having 3 valence electrons and Beryllium is having 2 valence electrons in its valence shell. We must need to know that the theory of hybridisation explains alkene and methane bonding.
Complete step by step answer:
Let’s start with discussing hybridisation, According to the concept in hybridization the orbitals of bond forming atoms fuse together to form a different orbital which are known as hybridised orbitals. These orbitals influence the molecular geometry and bonding stability of the molecule. The concept of hybridization is an expansion of the valence bond theory.
Now coming to the question, we are given 2 molecules which are BH3 and BeH2. In BH3 , Boron (B) is having only 3 electrons in its outer shell which means all these electrons are being used in bond formation. So the hybridization of the central atom B is sp2 and only one s orbital and 2 p orbital is being utilized. The last p orbital is vacant.

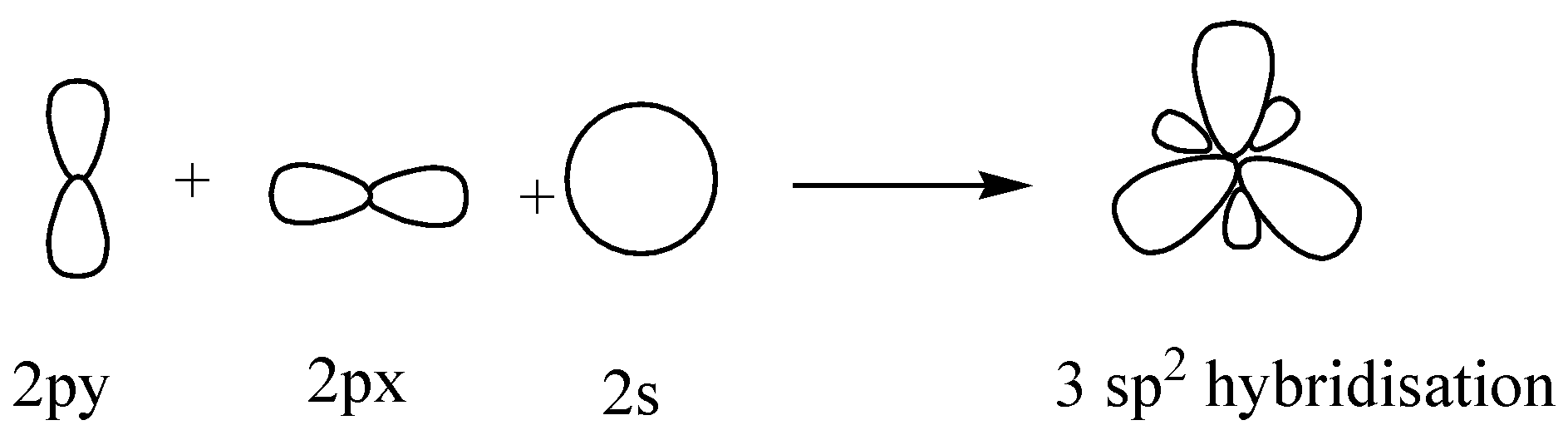

Similarly in the case of BeH2 , only 2 bonds are being formed and the hybridization is ‘sp’.
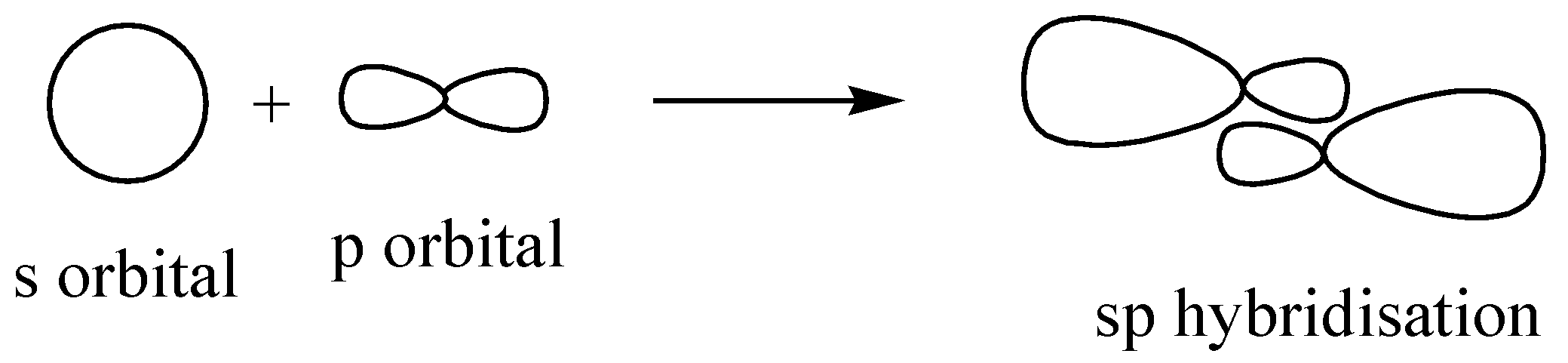
We can proceed in another way as well, beryllium (Be) is having only 2 valence electrons and hydrogen is having only 1. The number of hydrogen attachments is 2. So the total number of electrons in bond formation is 4. This implied
24=2 , divided by two because of hydrogen, if any other atom then it will be 8.
So, the correct answer is Option D.
Note: We must know that the hybridisation theory is an integral part of organic chemistry, with Baldwin’s rules being one of the most compelling examples. A classical bonding image is sometimes needed for drawing reaction mechanisms with two atoms sharing two electrons. The amount of p character or s character, which can be determined by orbital hybridization, we can use to predict molecular properties such as acidity or basicity reliably.
