Question
Question: The state of hybridization of boron and oxygen atom in boric acid \(\left( {{H_3}B{O_3}} \right)\) i...
The state of hybridization of boron and oxygen atom in boric acid (H3BO3) is respectively:
A.sp3,sp3
B.sp2,sp3
C.sp3,sp2
D.sp2,sp2
Solution
We can determine the hybridization of an atom in a molecule, using steric numbers. We can calculate the steric number by summing up the number of atoms bonded to the central atom and the lone pairs of electrons on the central metal atom. Let us know that if the steric number is 4, then we say the atom is in sp3 hybridization, if the steric number is 3, then it is sp2 hybridization, if the steric number is 2, then it is sp hybridization.
Complete step by step answer: We know the formula of boric acid is H3BO3. we can draw the structure of boric acid as,
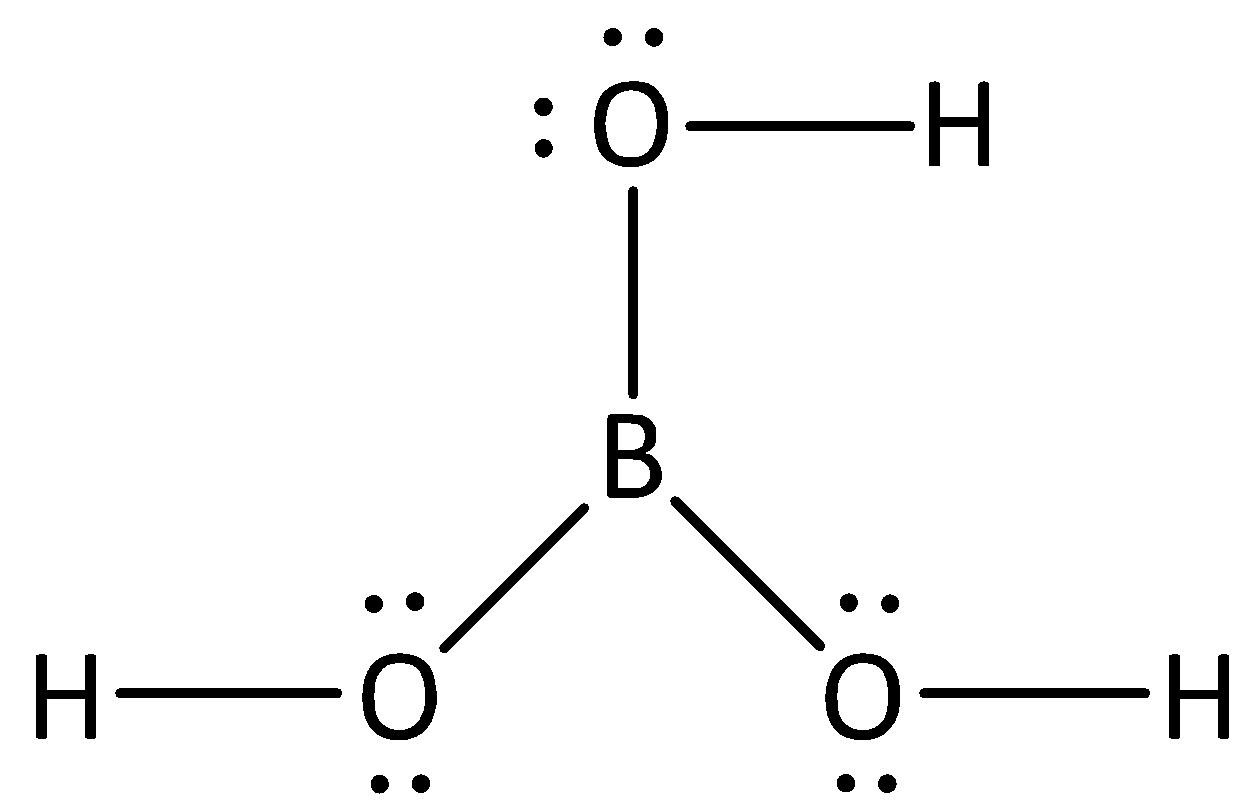
The steric number of boron atoms can be calculated by adding the number of atoms present in the central metal atom and lone pairs present in the central metal atom.
We can calculate the steric number of boron as,
We have calculated the steric number of boron is 3. If an atom has steric number 3, we have to know that hybridization of atom will be sp2.
Therefore, the hybridization of boron boric acid is sp2.
In the structure of boric acid, we can see that the oxygen atoms consists of two bond pairs and two lone pairs, therefore the total number of groups present in oxygen is four, and if the number of groups present is four, then the hybridization of atom will be sp3.
Therefore, the hybridization of oxygen in boric acid issp3.
Boric acid contains a network complex structure, and the geometry of boron is trigonal planar and is sp2 hybridized whereas the geometry of oxygen is tetrahedral and has sp3 hybridization with two lone pairs of electrons present in each atom of oxygen.
∴Option B is correct.
Note:
We can also determine the hybridization for organic molecules in the following method,
-If an atom contains single bonds, then it is sp3 hybridized. Example for sp3 hybridized molecule is methane. Generally, alkanes come under sp3 hybridization. Molecules that have sp3 hybridization will have tetrahedral geometry.
-If an atom contains double bonds, then it is sp2 hybridized. Example for sp2 hybridized molecule is ethene. Generally, alkenes come under sp2 hybridization. Molecules that have sp2 hybridization will have trigonal planar geometry.
-If an atom contains triple bonds, then it is sp hybridized. Example for sp hybridized molecule is ethyne. Generally, alkynes come under sp hybridization.
