Question
Question: The standard molar enthalpies of formation of cyclohexane (l) and benzene (l) at \({ 25 }^{ \circ }{...
The standard molar enthalpies of formation of cyclohexane (l) and benzene (l) at 25∘C are −156 and 49kJmol−1 respectively. The standard enthalpy of hydrogenation of cyclohexene (l) at 25∘C is −119kJmol−1. Use this data to estimate the magnitude of the resonance energy of benzene.
Solution
To answer this, you must know what enthalpy of formation and heat of hydrogenation is.
Remember that resonance energy is given by ΔHobs−ΔHcal. To find this, use the formula-
ΔHcal=ΔHf of cyclohexane−ΔHf of benzene+3×ΔHf of H2 and remember that ΔHobs is the observed value which you can find out from the standard enthalpy of hydrogenation of cyclohexene.
Complete Solution :
Firstly, let us discuss what hydrogenation and enthalpy of formation is.
At these standard conditions we can define the standard enthalpy of formation as the change of enthalpy of during the formation of 1 mole of the substance where all the substances are in their standard states.
Hydrogenation of alkenes simply means addition of hydrogen atoms across the double bonds. The product thus formed has a carbon-carbon single covalent bond and is known as an alkane. Addition of hydrogen atoms across the double bond will cause loss of a bond.
Now, we can see that in the question, it is given to us that-
Standard molar enthalpy of formation of cyclohexane = −156kJmol−1
Standard molar enthalpy of formation of benzene = 49kJmol−1
Standard enthalpy of hydrogenation of cyclohexene = −119kJmol−1
Now, if we write the reaction for these processes according to the definition, it will be-
6C+6H2→C6H12;ΔH=−156kJmol−1
6C+3H2→C6H6;ΔH=49kJmol−1
C6H10+H2→C6H12;ΔH=−119kJmol−1
We have to find out the resonance energy of benzene i.e. we have to calculate -
C6H6(l)+3H2→C6H12; ΔH=?
- Now, ΔH can be calculated by-
ΔHobs=ΔHf of cyclohexane−ΔHf of benzene+3×ΔHf of H2
ΔHcal = [−156−(+49)+03]
ΔHcal = −205kJmol−1
Since the double bond of cyclohexane is hydrogenated and its standard enthalpy of hydrogenation = −119kJmol−1
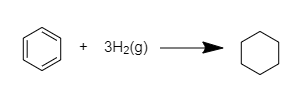
In this, three C=C bonds are present in benzene and by hydrogenation, they can change into benzene.
Thus, the ΔH of this heat of hydrogenation = 3×(−119kJmol−1)= −357kJmol−1
As we know resonance energy = ΔHobs−ΔHcal
= [−357−(−205)] = −152kJmol−1
Hence, the resonance energy of benzene = −152kJmol−1
Additional Information:
- The heat of hydrogenation is the amount of heat released during the hydrogenation of an alkene. It depends on the stability of the carbon.
- The less stable i.e. less substituted carbon will have a higher heat of hydrogenation whereas the more stable i.e. more substituted carbon will have less heat of hydrogenation.
Note: The possibility to make a mistake is that when you calculate ΔHobs , three hydrogens are required for hydrogenation, so you have to multiply the standard enthalpy of hydration with three to calculate this heat of hydrogenation.
