Question
Question: The stability order of the following singlet halocarbene is: (A)\(C{{F}_{2}}\)>\(CC{{l}_{2}}\)>\(C...
The stability order of the following singlet halocarbene is:
(A)CF2>CCl2>CBr2>CI2
(B) CI2>CBr2>CCl2>CF2
(C) CCl2>CF2>CBr2>CI2
(D) CF2>CI2>CCl2> CBr2
Solution
Hint One type of carbon cations without a formal charge is carbine and the other valence electron in nonbonding pair orthogonal to the πsystem. Carbenes can act as both electrophile and nucleophile. Both triplet methylene and singlet methylene are sp2 hybridizations with bent shape and bond angles are 1250−1400 and 1020 respectively
Complete step by step solution:
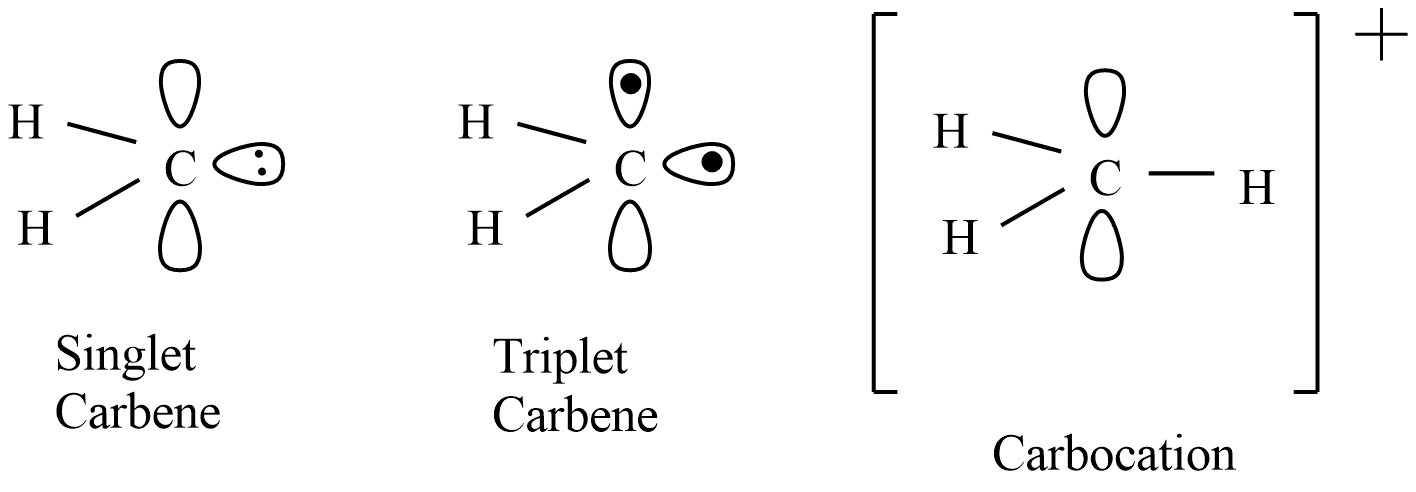
The singlet carbene is the lowest energy than triplet carbene, which means singlet carbene is the excited state spice and triplet carbene is a more stable state. This stability of carbenes decreases in the inductive withdrawal while stabilizes onπ- orbital donation capability.
The single carbene will stabilize with substituents that can donate electron pairs like halogens by delocalizing the pair into an empty p-orbital. Due to the unavailability of vacant orbital at carbon, no corresponding stabilization possible for triplet carbene. So, the singlet carbene is more stable than the triplet carbene when there is a substituent with lone pairs in the singlet carbene.
Therefore, the order of stability of singlet carbene as follows,
Cl2<CBr2<CCl2<CF2<CH2
The order of stability of triplet carbene as follows,
Cl2>CBr2>CCl2>CF2>CH2
Hence, the stability order of the following singlet halocarbene is,
CF2>CCl2>CBr2>CI2
Thus, the correct answer is option A.
Note: Singlet carbene cannot do things like triplet carbenes do, because triplet carbene is highly reactive diradical. But singlet carbenes are not radicals. There is one electron in the usually full orbital and one in the empty orbital called triplets which determine triplets reactivity with olefins in cyclopropanation reactions
