Question
Question: The stability of the ferric ion is due to: A) half-filled d-orbitals B) half-filled f-orbitals ...
The stability of the ferric ion is due to:
A) half-filled d-orbitals
B) half-filled f-orbitals
C) completely filled d-orbitals
D) completely filled f-orbitals
Solution
Polyacrylonitrile is a polymer. A molecule that can react with other molecules to form very large molecules having high molecular weights is known as a monomer. The high molecular weight molecules formed are known as polymers. The monomer is a repeating unit of polymer.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Iron is the 3d series element having an atomic number is 26, which indicates there are 26 electrons are there in the iron. There are two main ions formed by the iron: ferric and ferrous ions. The ferric ion is Fe3+ and ferrous ion is Fe2+. These ions are formed by the loss of the valence electrons from the neutral iron atom.
As we know the electronic configuration of the iron is represented as follows:
Fe[Ar]3d64s2
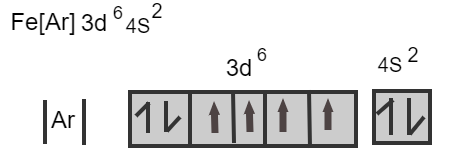
Iron losses three electrons from its neutral atom leads to the form Fe3+ ion known as a ferric ion.
Fe+3[Ar]3d54s0
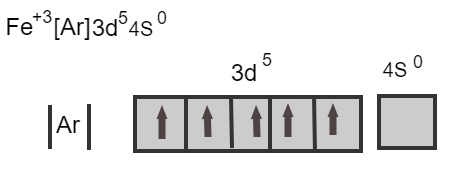
Here, two electrons from the 4s orbital and one electron from the 3d orbital is removed and there are five electrons in the d orbital. The maximum capacity of the d orbital is ten electrons, as there are five electrons it is a half-filled orbital.
If the valence orbital of an atom or ion is either completely filled or half-filled such an ion or atom is stable. Here, in the case of the ferric ion d orbital is half-filled which gives stability to the ferric ion.
Therefore, option (A) is the correct answer to the question. Now, in option (B) it is given that half-filled f orbitals is an incorrect option because there are no f orbitals in the ferric ion.
Here, option (C) is also incorrect as in ferric ion there are no completely filled d orbitals.Now, option (D) is also incorrect because of the absence of the f orbitals in the ferric ion.
Note: In most of the ions or atoms stable electronic configuration is the noble gas electronic configuration in which all the valence orbitals are either completely filled. In some ions, the extra stability of the ion is attained because of the half-filled valence orbitals. In this way ions or elements with either half-filled or completely filled orbitals are stable.
