Question
Question: The source of EcoRI? A. _Escherichia coli RI_ B. _Escherichia coli RI13_ C. _Escherichia coli ...
The source of EcoRI?
A. Escherichia coli RI
B. Escherichia coli RI13
C. Escherichia coli RY13
D. Escherichia coli RX13
Solution
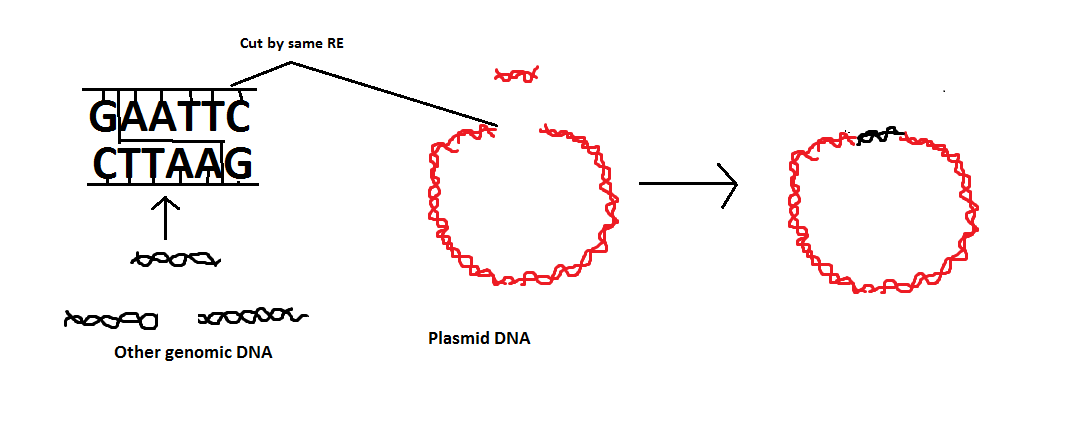
Eco RI is a restriction endonuclease enzyme that is used in genetic engineering.
Restriction enzymes cleave the DNA at a specific nucleotide sequence that is called recognition site.
Complete answer: The source of Eco RI is Escherichia coli RY13. Eco RI is a restriction enzyme that cuts the DNA at a specific site. We can use these to isolate our desired gene from a number of genes. A restriction enzyme cuts the DNA only at one recognition site. On these sites, the palindrome sequence is found. Palindrome sequence is a sequence that has the same base sequence at both strands. The restriction enzyme EcoRI cuts the DNA at ‘GAATTC’. A specific nucleotide sequence of DNA is recognized only by one restriction endonuclease, not by others. These restriction endonuclease enzymes are found in bacteria. These enzymes inhibit the growth of bacteriophage in bacteria by cutting its genetic material. So, these enzymes are isolated from bacteria. HindIII enzyme was the first enzyme to be discovered from this category. Now, more than 900 enzymes are discovered and isolated from various strains of bacteria. The nomination of restriction enzymes is done according to the name of bacteria from which it has been isolated. Eco RI is isolated from Escherichia coli RY13. Here ‘E’ shows the genus name Escherichia , ‘co’ shows the name of species coli and ‘R’ shows the strain of bacteria. The number ‘I’ shows that this was the first isolated enzyme from this strain. DNA sticky ends are made by using these enzymes and are used in recombinant DNA technology. The same restriction enzyme is used for both the plasmid and the DNA fragment that has to be cleaved.
Hence, the correct answer is option C.
Note: Most important characteristics of a restriction enzyme is that it does not matter from what source they are isolated. They are equally active in the DNA of all organisms. We can isolate these enzymes from bacteria and use them for the fungal incorporation.
